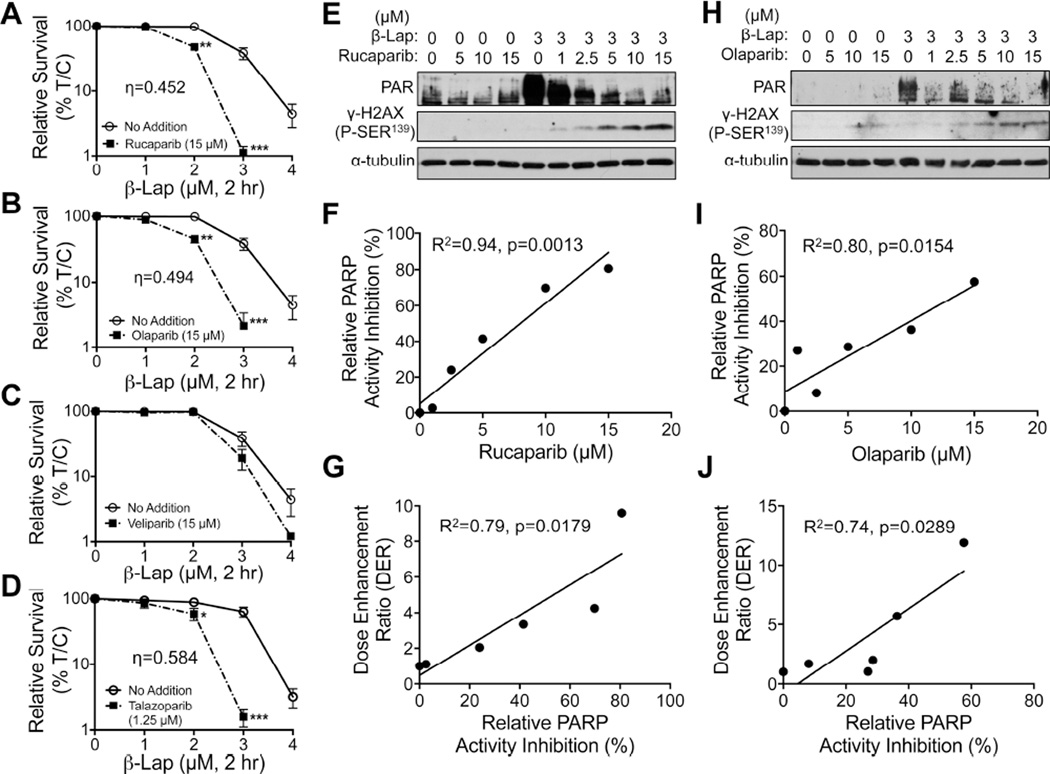
Figure 3. Synergy between nontoxic doses of PARP inhibitors and sublethal β-lapachone doses.
(A–D) A549 NSCLC cells were pretreated for 2 hr with: Rucaparib (A), Olaparib (B), Veliparib (C), each at 15 µM, or Talazoparib at 1.25 µM (D), based on their relative toxicities alone (Figures S3A–S3D) followed by a 2 hr treatment with PARP inhibitor + various β-lap doses (Figures S3H–3K). Drugs were removed and survival assessed. All error bars are means ±SEM. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05 (t tests). Synergy was calculated as per (Chou and Talalay, 1984). Synergy values for Rucaparib (η=0.452, p value=0.003), (Olaparib (η=0.494, p value=0.0013) and Talazoparib (η=0.548, p value=0.036) were reported based on multiple dose-responses, or on comparative p values indicated. (E, H) PAR and γH2AX formation alterations for DMSO or β-lap (3 µM)-exposed A549 cells treated with various doses of Rucaparib (E) or Olaparib (H).
(F, I, G, J) Relative PARP activity inhibition for doses of Rucaparib (F) or Olaparib (I) and dose enhancement ratio (DER) correlations for Rucaparib (G) or Olaparib (J) dose-responses when combined with β-lap (3 µM).
See also Figure S3.