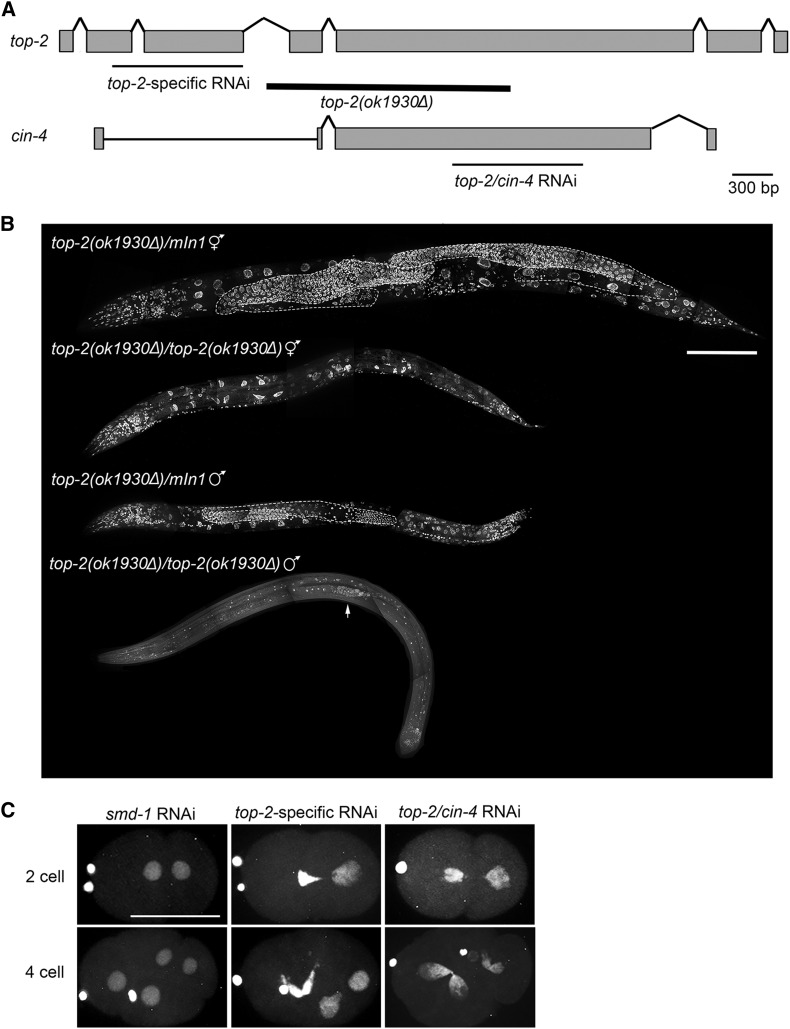
Figure 5.
top-2 is required for multiple cell cycles and developmental stages. (A) Schematic comparing the gene structure of top-2 and its paralog cin-4. Thick black line below the top-2 gene structure indicates the extent of the ok1930Δ deletion. Thin black lines below the gene structures indicate the sequences targeted by either top-2-specific RNAi or the RNAi construct that targets sequences present in both genes. (B) Whole-mount top-2(ok1930Δ) and control top-2(ok1930Δ)/mIn1 hermaphrodites and males were prepared for imaging by methanol fixation and DAPI staining. A minimum of three animals of each genotype were imaged. Germ lines in the heterozygous control animals are outlined in white. Arrow points to the few mitotic germ cells generated in the top-2(ok1930Δ) homozygous mutant male. Bar, 100 μm. (C) top-2 RNAi causes segregation defects in the early embryo. L3 hermaphrodites expressing mCherry::H2B were plated on RNAi plates at 24° for 24 hr. Hermaphrodites were dissected and embryos imaged with a confocal microscope. 0% of two-cell (n = 16) and four-cell (n = 16) smd-1 RNAi embryos scored had the cross-eyed phenotype. Of the top-2-specific RNAi embryos scored, 75% of two cell (n = 32) and 81.6% of four cell (n = 38) had the cross-eyed phenotype. 62.7% of two-cell (n = 51) and 81.8% (n = 33) of four-cell top-2/cin-4 RNAi embryos had the cross-eyed phenotype. Bar, 30 μm.