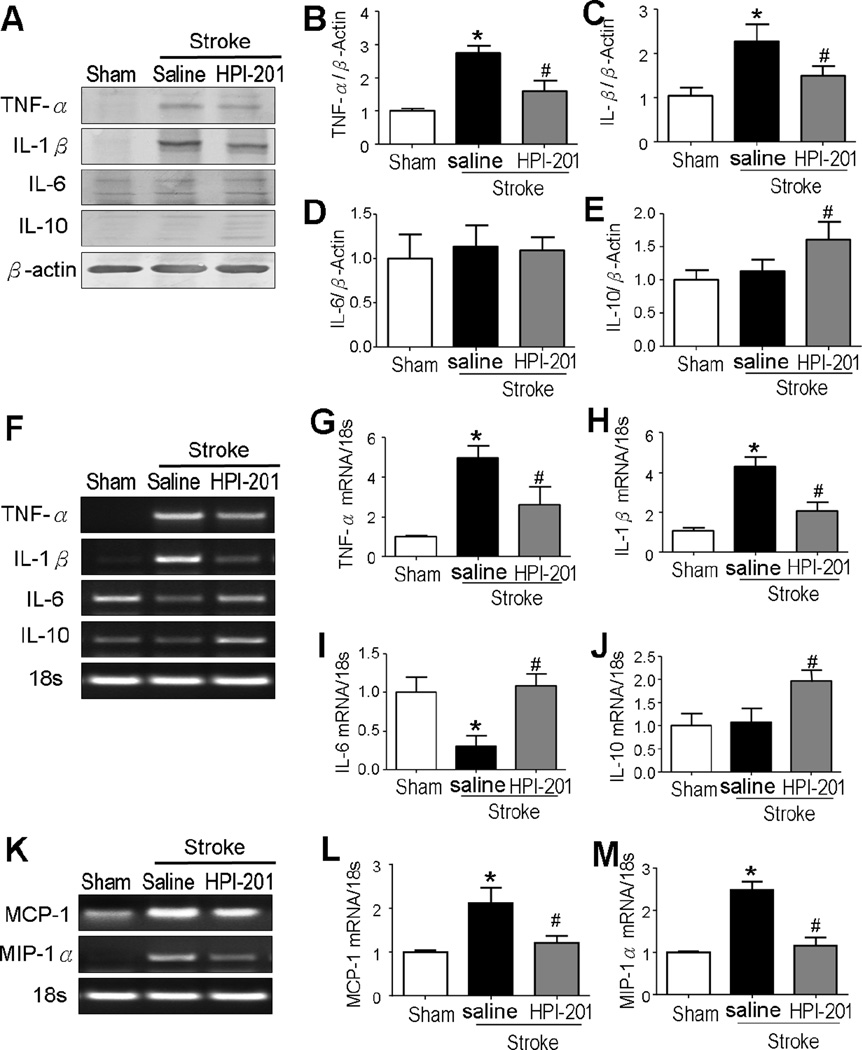
Figure 2. TH altered cytokine expressions in the ischemic brain.
Protein expressions (A to E) and mRNA levels (F to M) of cytokines were measured using Western blot and RT-PCR analyses in the penumbra tissue at 3 days after stroke. A to C. Stroke induction significantly enhanced expression of the pro-inflammatory proteins TNF-α (A and B) and IL-1β (A and C), which was attenuated by the HPI-201 treatment. D. No change was observed in the anti-inflammation cytokine IL-6 between groups after stroke. E. Stroke did not induce the expression of IL-10, while HPI-201 showed a significant increase in IL-10 expression. * P<0.05 versus sham controls; #P<0.05 versus stroke controla; n=3 in sham group, n=5 in stroke and stroke plus HPI-201 groups, respectively. F to J. RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines showed that stroke induction increased pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA, while HPI-201 largely prevented these increases (G and H). Reduced IL-6 mRNA was seen in the stroke brains, while HPI-201 maintained the IL-6 mRNA expression at normal levels (I). There was no change in the anti-inflammation cytokine IL-10 after stroke, while HPI-201 treatment enhanced IL-10 mRNA expression (J). * P<0.05 versus sham group; # P<0.05 versus stroke group; n=3–5 per group. K to M. RT-PCR analysis of chemokines showed upregulations of MCP-1 and MIP-1α after stroke, which were blocked by HPI-201 treatment. * P<0.05 versus sham group; # P<0.05 versus stroke group; n=5 per group.