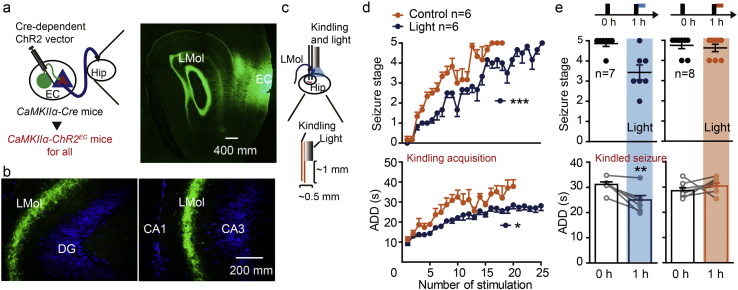
Fig. 5.
Activation of the projection fibers of entorhinal CaMKIIα-positive neurons reduces the severity of hippocampal seizures. a) ChR2-eYFP-labeled fibers mainly projected to the lacunosum-moleculare layer (LMOL) of the hippocampus in CaMKIIα-ChR2EC mice. b) Representative ChR2-eYFP-labeled fibers in the section of hippocampus. c) The electrode design used for photo-stimulation of the hippocampal LMOL and kindling electrical stimulation of the ventral hippocampus. Electrical stimulation electrode for kindling is 1.0 mm lower than the optical fiber, which is just about the distance between the LMOL and the CA3 kindling focus. d) Low-frequency blue light stimulation (473 nm, 1 Hz) of the LMOL retarded the development of seizure stage (above) and ADD (below) during hippocampal kindling acquisition. (Two-way ANOVA for repeated measures followed by LSD post hoc test). The control group received yellow light stimulation (593 nm, 1 Hz). e) Low-frequency blue light stimulation (473 nm, 1 Hz) of the LMOL lowered the seizure stage (above) and shortened the ADD (below) in kindled mice (paired t-test). Black rectangle indicates kindling stimulation, the blue rectangle indicates blue light stimulation, and the yellow rectangle indicates yellow light stimulation. Mice were treated with blue light stimulation (473 nm, 1 Hz) and yellow light stimulation (593 nm, 1 Hz; yellow light self-control). Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared to the control or baseline.