Figure 8.
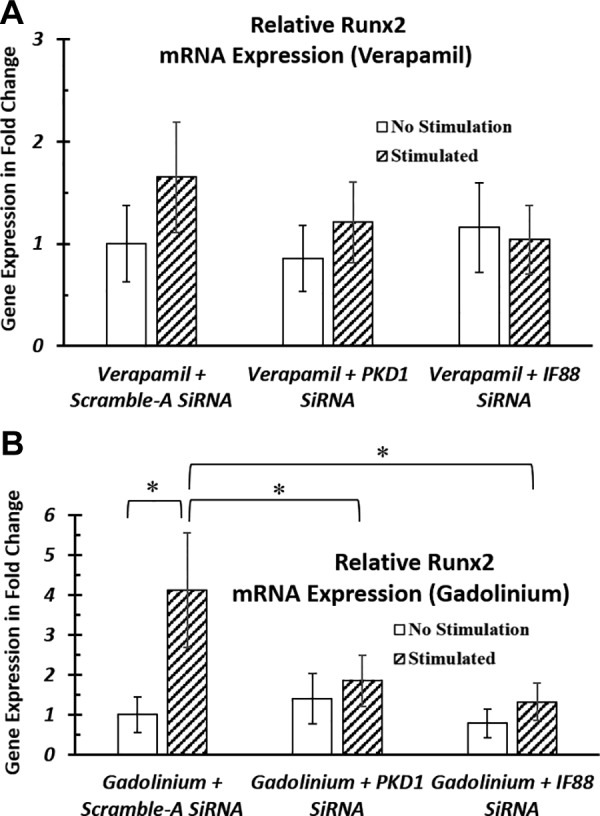
Involvement of calcium channels during primary cilia–mediated EFS. A, B) After siRNA knockdown, hASCs were transferred into ODM that was supplemented with verapamil (A), a voltage-gated ion channel blocker, or gadolinium (B), a stretch-activated ion channel blocker. hASCs were stimulated with 1 V/cm electric field at 1 Hz for 4 h. After blocking the voltage-gated channels, further knocking down primary cilia proteins did not affect electrical stimulation–induced osteogenic response in hASCs (A). In contrast, after blocking stretch-activated calcium channels in hASCs, there was still a significant decrease in stimulation effect when further knocking down primary cilia structural proteins (B). RNA was extracted and analyzed at the end of electrical stimulation. mRNA expressions were normalized to negative control siRNA-transfected nonstimulated samples. *P < 0.05.
