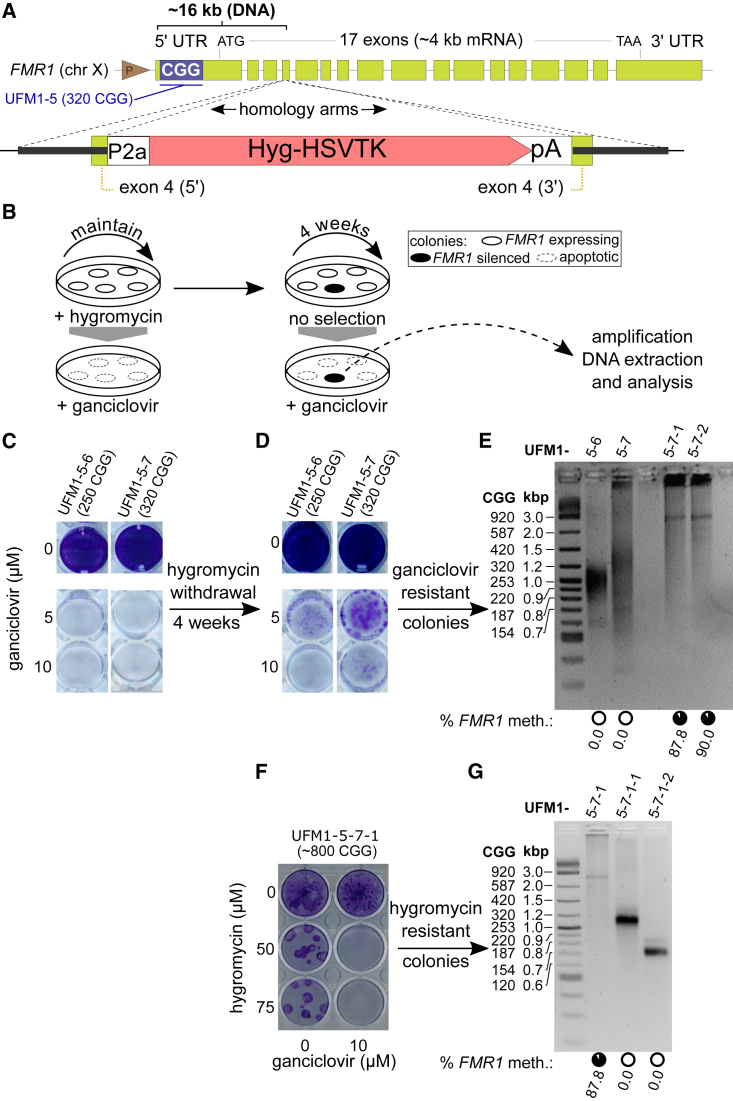
Figure 4.
Gain in CGG Repeat Number Is Coupled with FMR1 Silencing in UFM iPSC Clones
(A) Strategy to target a hygromycin resistance-HSV thymidine kinase (HyTK) positive/negative selection cassette into FMR1. In this setup transgene expression is driven by the endogenous FMR1 promoter. See also Figure S3.
(B) Experimental design to select for iPSCs that silence the FMR1 promoter driven HyTK. Continuous hygromycin administration selects for cells that express the transgene making them sensitive to ganciclovir. Four weeks without hygromycin allows appearance of cells that spontaneously downregulate the transgene. These cells can be selected for by ganciclovir treatment. Subsequent DNA analysis identifies clones with FMR1 promoter methylation events.
(C and D) Crystal violet staining of surviving cells after ganciclovir treatment of two knockin iPSC clones (UFM1-5-6 and UFM1-5-7) that were maintained: (C) under hygromycin selection or (D) without hygromycin selection for 4 weeks.
(E) DNA methylation status and number of CGG repeats of FMR1 from knockin iPSC lines before and after hygromycin withdrawal and subsequent ganciclovir selection. Lanes UFM1-5-6 and UFM1-5-7 are the original clones before hygromycin withdrawal. Subclones UFM1-5-7-1 and UFM1-5-7-2 are derived from UFM1-5-7 after 4 weeks of hygromycin withdrawal and subsequent ganciclovir selection. Circles under each lane indicate mean percentage of DNA methylation across 22 CpGs of the FMR1 promoter for a given line based on data in Table S1. Two ganciclovir-resistant clones, UFM1-5-7-1 and UFM1-5-7-2, gained ∼90% methylation and have increased CGG repeats (∼800 CGG) compared with the parental UFM1-5-7 (320 CGG). See also Figure S4.
(F) Crystal violet staining of surviving cells after hygromycin treatment of ganciclovir-resistant subclone UFM1-5-7-1. For cells maintained with ganciclovir, no surviving colonies are observed. Upon ganciclovir withdrawal, spontaneous reactivation of FMR1 promoter is possible and appearance of surviving colonies is observed.
(G) Analysis of two hygromycin-resistant colonies obtained from subclone UFM1-5-7-1 after withdrawal of ganciclovir as indicated in (F). Parental clone UFM1-5-7 is analyzed in the first lane for direct comparison. CGG repeat sizes 320 and 150 indicate contraction events. Black circles under each lane indicate mean percentage of DNA methylation across 22 CpGs of the FMR1 promoter based on data in Table S1. No methylation is observed in the surviving colonies, indicating that contraction below the silencing threshold is associated with loss of DNA methylation.