Figure 1.
PRDM14 Induces the Transition of EpiLCs to ESCLCs
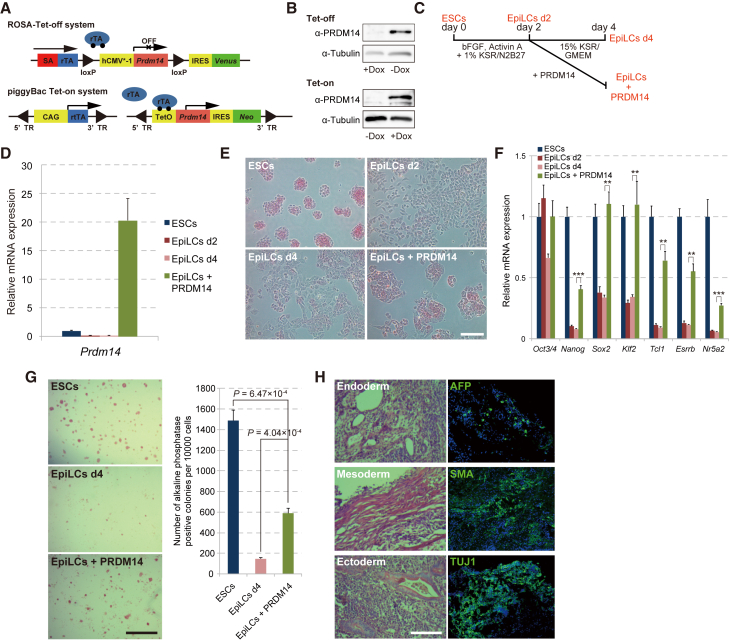
(A) Constructs of the ROSA-Tet-off system and piggyBac Tet-on system.
(B) Western blotting of PRDM14 and tubulin.
(C) Scheme of the transition of ESCs to EpiLCs and of EpiLCs to ESCLCs.
(D) qRT-PCR analysis of Prdm14 expression in ESCs, EpiLCs (d2), EpiLCs (d4), and EpiLCs + PRDM14. Error bars indicate ±SD of a biological triplicate.
(E) AP staining of ESCs, EpiLCs (d2), EpiLCs (d4), and EpiLCs + PRDM14. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(F) qRT-PCR analysis of pluripotency genes in ESCs, EpiLCs (d2), EpiLCs (d4), and EpiLCs + PRDM14. Error bars indicate ±SD of a biological triplicate.
(G) Colony formation by ESCs, EpiLCs (d4), and EpiLCs + PRDM14 was assessed by AP staining over 3 days in the presence of serum + LIF. Error bars indicate ±SD of biological triplicates. p Values were calculated with the Student's t test. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(H) (Left) Teratoma formation by EpiLCs expressing Prdm14 cultured in the absence of LIF. (Right) Immunofluorescent staining of α-fetoprotein (AFP), smooth muscle actin (SMA), and class III β-tubulin (TUJ1) in teratoma sections. Scale bar, 200 μm.
∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, Student's t test.