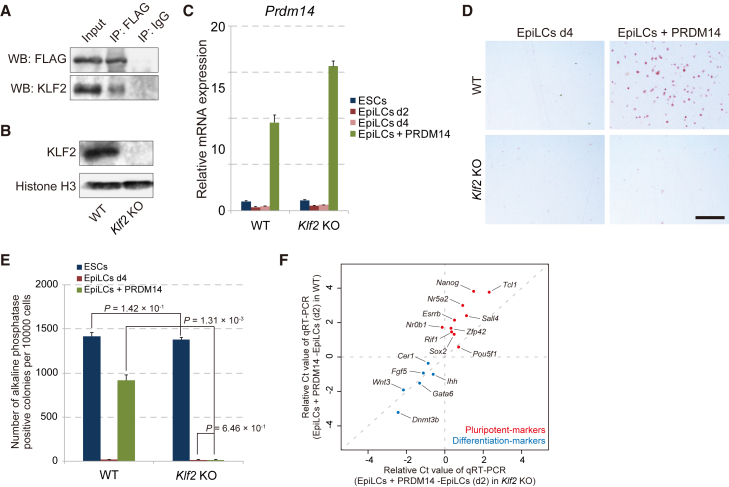
Figure 3.
Klf2 Is Required for the PRDM14-Induced Reversion of EpiLCs to ESCLCs
(A) Immunoprecipitation of PRDM14 with KLF2 in ESCs.
(B) Western blot analysis of KLF2 expression in WT and Klf2 KO ESCs.
(C) qRT-PCR analysis of Prdm14 expression in WT and Klf2 KO ESCs. Error bars indicate ±SD of a biological triplicate.
(D) Colony formation by EpiLCs with or without Prdm14 induction induced from WT or Klf2 KO ESCs, as assessed by AP staining. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(E) Quantification of colony formation shown in (D). Error bars indicate ±SD of biological triplicates. p Values were calculated with Student's t test.
(F) Scatter plot shows relative Ct values of pluripotency-associated genes (red dots) and differentiation markers (blue dots) determined by qRT-PCR. The x axis indicates relative Ct values of each gene (EpiLCs + PRDM14 − EpiLCs [d2]) in WT, and the y axis indicates relative Ct values of each gene (EpiLCs + PRDM14 − EpiLCs [d2]) in Klf2 KO.