Figure 1. Overview of the ligand-dependent modulation of ERα activity.
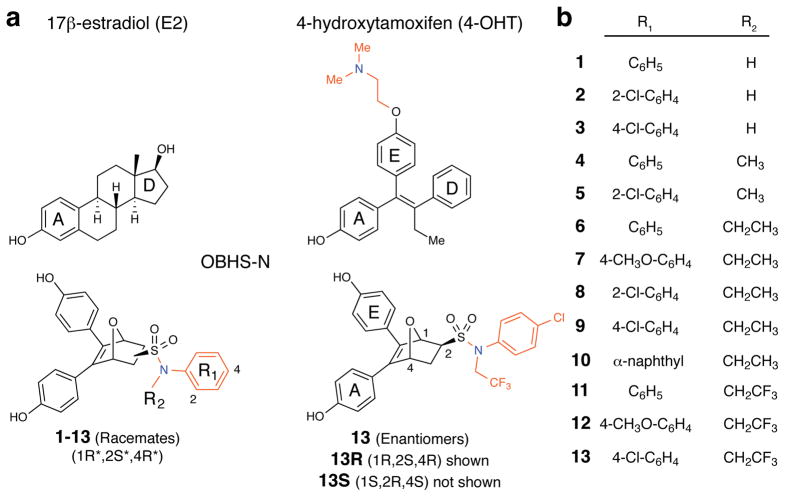
(a) Structures of 17β-estradiol (E2), 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT), and the OBHS-sulfonamides (OBHS-N). The ring designations A, D and E are given to facilitate comparisons among these structures. In the OBHS-N structures, a helix-11 (h11)-directed aryl group, R1, was attached to the ligand core via a sulfonamide linker, which provided a site to affix a second h11-directed functional group, R2. Locant numbers 1, 2, and 4 for stereochemical designations are on the 7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene core (see lower right structure), and locant numbers 2 and 4 on the R1 ring (lower left structure) are the locations of the substituents listed in panel b.
(b) List of OBHS-N analogs (1–13). All 13 analogs have the 1R*,2S*,4R* relative configuration in the 7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene core and were prepared and tested as racemates (i.e., a 1:1 mixture of 1R,2S,4R and 1S,2R,4S enantiomers). In addition, both enantiomers of analog 13, designated 13R and 13S, were isolated by chiral HPLC and were also tested individually.