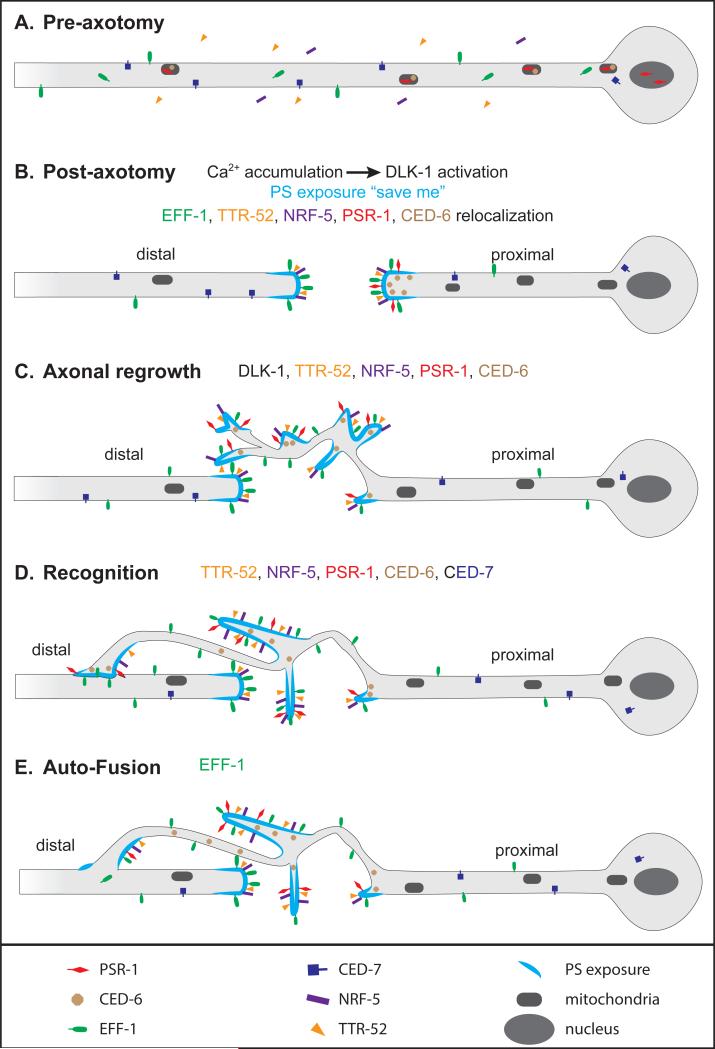
Figure 2. Model of axon reconnection by auto-fusion.
Model based on refs. [3, 69, 71]. (A) Before axotomy, PSR-1 (red) localizes in mitochondria and in the nucleus, and CED-6 (brown) localizes in mitochondria only. EFF-1 (green) is both intracellular and on the plasma membrane. (B) Immediately after axon injury, calcium is released and phosphatidylserine (PS, light blue) is exposed to the external lipid layer. Calcium release induces DLK-1 activation to promote axon regrowth. PSR-1 and CED-6 accumulate at the proximal tip. TTR-52 (orange), NRF-5 (purple) and EFF-1 accumulate on external membranes at both proximal and distal tips. (C) DLK-1 and the phagocytosis pathway promote axonal regrowth. (D) The phagocytosis pathway promotes recognition of distal axon by the proximal growth cone. (E) EFF-1 stimulates auto-fusion to reconnect the proximal part to the distal part of the axon.