Figure 3. Seamless tubes formed by auto-fusion can have complex shapes.
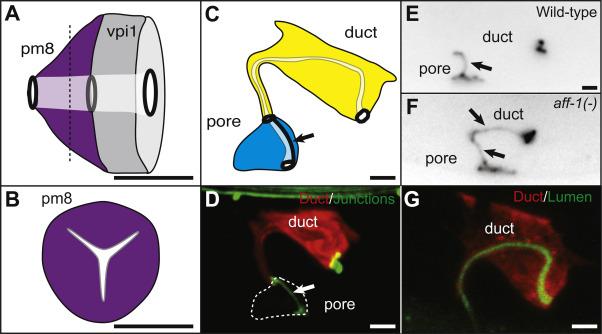
(A) Lateral view of C. elegans pharyngeal-intestinal valve cells (pm8 and vpi1), which are both seamless tubes. The tubes are linked to neighbors by ring-shaped junctions (black ovals). (B) A transverse section of pm8 (dashed line in A) shows the tri-radiate shape of the lumen [5]. (C) The C. elegans excretory duct is a seamless tube, in contrast to the adjacent cell, the excretory pore, which maintains an auto-junction (arrow). Both tubes are linked to neighbors by ring-shaped junctions (black ovals). (D) The excretory duct has an elongated shape. Red, duct cytoplasmic marker lin-48pro::mRFP [85]. Green, junction marker AJM-1::GFP [99]. (E, F) AFF-1 is required for duct seamlessness. Cell junctions marked by AJM-1::GFP. (E) Wild-type excretory duct is a seamless tube. (F) In an aff-1 loss of function mutant, the excretory duct is a seamed tube with an auto-junction (arrows) [6]. (G) The excretory duct has an elongated lumen. Red, duct cytoplasmic marker lin-48pro::mRFP. Green, luminal marker let-653pro::LET-653::GFP [100]. Scale bars. 2 μm.
