Figure 3. Adult fin phenotypes of hox13 deletion series.
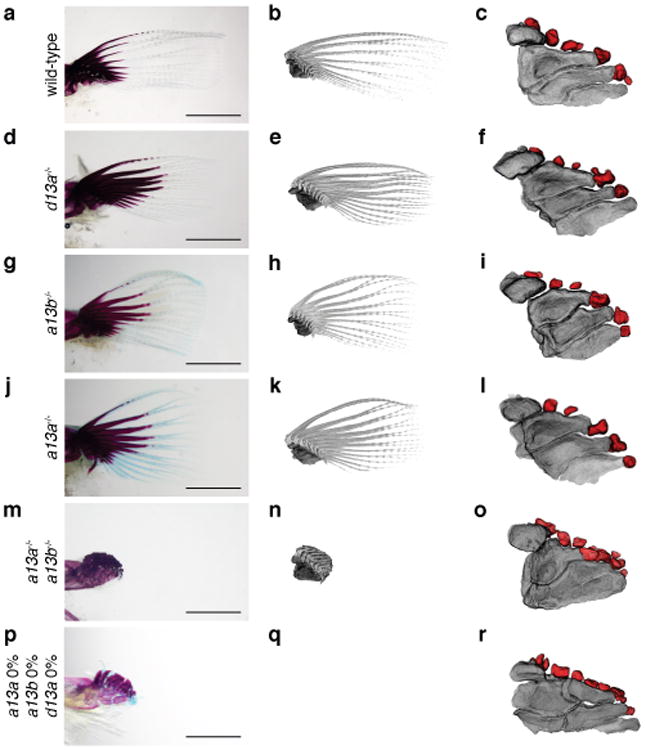
a-c, wild-type. d-f, hoxd13a-/-. g-i, hoxa13b -/-. j-l, hoxa13a-/-. m-o, hoxa13a-/-, a13b-/-. p-r hoxa13a0% a13b0% and d13a 0% (mosaic triple knockout; Methods and Extended Data Table 3,4). Each mutant hox sequence is found in Extended Data Table 3,4. a, d, g, j, m, p, Alzarin Red and Alcian Blue staining of pectoral fin. b, e, h, k, n, q, CT scanning of pectoral fins. Black: radials (endochondral bones); gray: fin rays (dermal bones). Note that hoxa13 single (g, h, j, k), double (m, n), and mosaic triple (p, q) mutant fins show shorter fin rays than wild-type (a, b). Fins were scaled according to the bone staining pictures. c, f, i, l, o, r, Enlarged images of CT scanning without fin rays to reveal endochondral patterns. Dark gray; proximal radials, red; distal radials. Upper left side is the anterior and bottom right is the posterior side in each pictures. Double and triple knockout mutants have 10-13 distal radials (o and, r, Extended Data Fig. 5, Supplementary Information). Third and fourth proximal radials started to fuse into one bone in hoxa13a-/-, a13b-/- (o). Note that posterior distal radials are stacked along proximodistal axis (o). Posterior proximal radials are broken down into small parts in mosaic triple knockout (r). Scale bars are 2 mm. The size of specimens are not scaled in c, f, i, l, o and r to display the detail of distal radials. n = 3 fish for single and double mutants and n = 5 fish for mosaic triple mutant.
