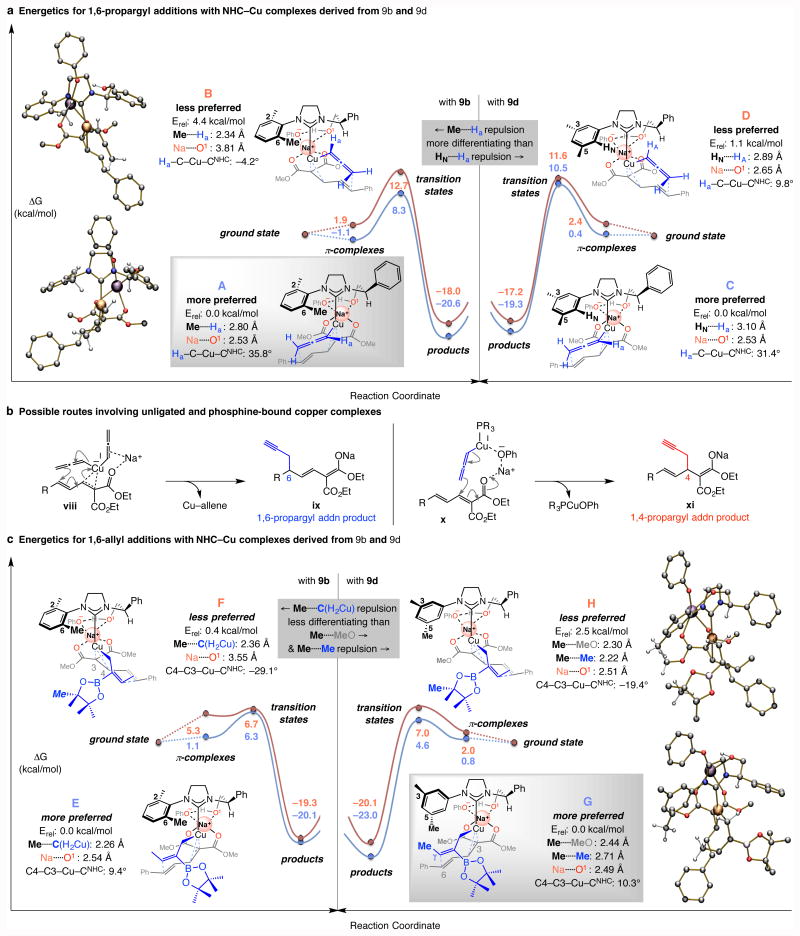
Figure 4. Mechanistic considerations.
a, Based on DFT calculations [ωB97XD/Def2TZVPP//ωB97XD/Def2SVP level of theory (THF)] stereochemical models were developed for NHC–Cu-catalyzed 1,6-propargyl additions with catalysts bearing an N-mesityl moiety (from 9b). The issue is the larger energetic differentiation arising from steric repulsion between an o-methyl unit of the N-aryl group and the allenylcopper moiety (i.e., Me⋯.Ha, 9b) versus one involving an aryl proton (i.e., HN⋯.Ha, 9d). b, Routes by which a phosphine–based and non-ligated Cu complex might generate products, respectively. c, Transition state energies for enantioselective allyl additions are consistent with the observation that the catalyst derived from 9d is optimal (vs. 9b). Steric repulsion involving a meta-methyl group of the NHC ligand with the carboxylic ester and the allylcopper substituents are the distinguishing elements. See the Supplementary Information for details of calculations. Abbreviations: NHC, N-heterocyclic carbene; Erel, relative energy.