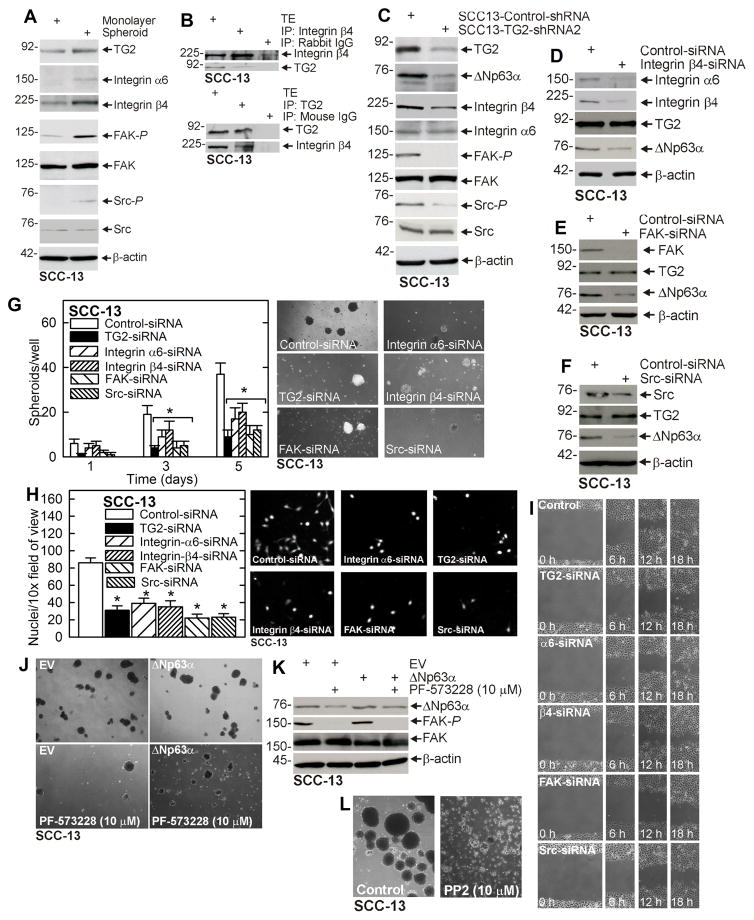
Fig. 2. α6/β4-Integrin signaling is essential for ΔNp63α expression.
A ECS cells display elevated α6/β4-integrin levels and elevated FAK/Src signaling. SCC-13 cells (40,000 per well) were grown in spheroid medium in attached (monolayer) or non-attached (spheroid, ECS cell). Cells were collected after 10 d and lysates were prepared for immunoblot. B SCC-13 cells spheroid were grown for 8 d and extracts were immunoprecipitated as indicated prior to immunoblot. C Integrin signaling is reduced in SCC13-TG2-shRNA2 cells. Cells were grown in spheroid medium in monolayer culture for 10 d prior to collection of lysates for immunoblot. D/E/F SCC-13 cells were double-electroporated with Control- or Integrin β4-, FAK-, or Src-siRNA and 48 h later extracts were prepared for immunoblot. G/H/I SCC-13 cells were double-electroporated with the indicated siRNA and 24 h later plated for growth as spheroids and for invasion and migration assays. J/K/L Cells were double-electroporated with indicated plasmid (EV, empty vector or ΔNp63α plasmid) and 24 h later plated for spheroid formation in the presence of the indicated inhibitor. Spheroids were grown for 5 d and then photographed and extracts prepared for immunoblot. The plotted values are mean ± SEM and asterisks indicate significant change compared to control, n = 3, p < 0.005.