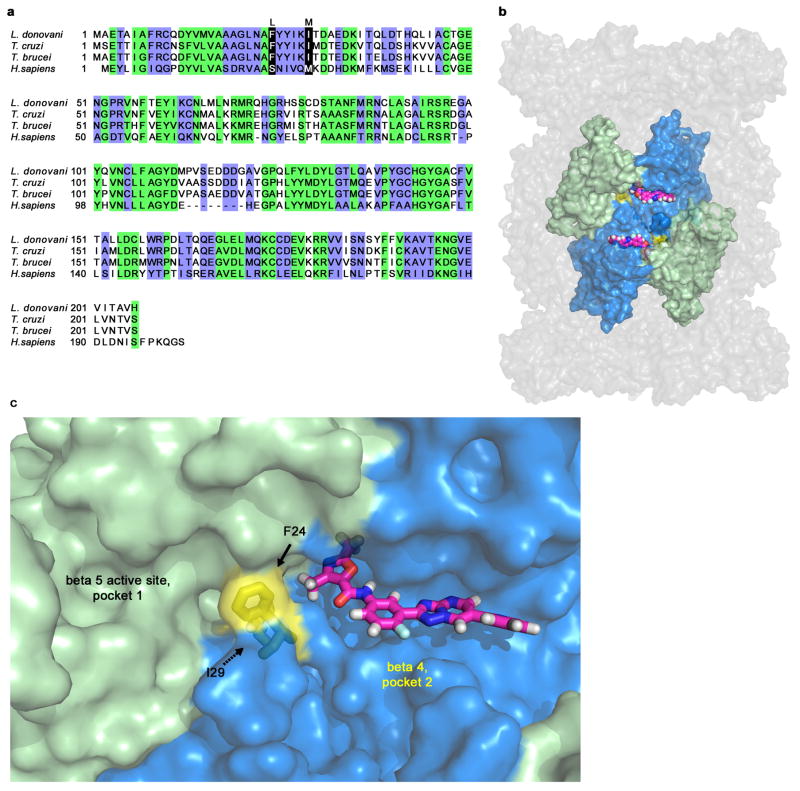
Extended Data Figure 6. Hypothetical model of GNF6702 binding to T. cruzi proteasome beta 4 subunit.
a, Alignment of amino acid sequences of proteasome beta 4 subunits (PSMB4) from L. donovani, T. cruzi, T. brucei and H. sapiens. Green: amino acid residues conserved between human and kinetoplastid PSMB4 proteins; blue: amino acid residues conserved only among kinetoplastid PSMB4 proteins; black: amino acids mutated in T. cruzi mutants resistant to analogues from the GNF6702 series. b, Surface representation of the modeled T. cruzi 20S proteasome structure showing relative positions of the beta 5 and beta 4 subunits. Beta 4 amino acid residues F24 and I29 (colored yellow) are located at the interface of the two beta subunits. GNF6702 is depicted in a sphere representation bound into a predicted pocket on the beta 4 subunit surface with carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen atoms colored magenta, blue, red and grey, respectively. The other T. cruzi 20S proteasome subunits are colored gray. c, Close-up of the beta 5 and beta 4 subunits. The beta 5 subunit active site (pocket 1, chymotrypsin-like activity) is colored pale green. The predicted beta 4 pocket (pocket 2) with bound GNF6702 is colored blue. The inhibitor is shown in a stick representation with atoms colored as described in caption for the b panel. Beta 4 residues F24 and I29 are colored yellow. The proteasome model shown in panels b and c was produced by The PyMol Molecule Graphics System, Version 1.8, Schrodinger, LLC.