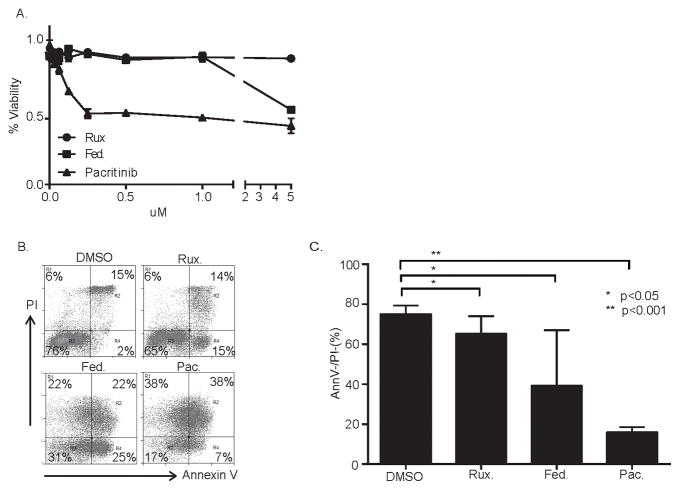
Figure 4.
Pacritinib inhibits monocyte-derived macrophage viability. (A) Monocytes were plated in triplicate wells of a flat-bottom 96-well plate supplemented with CSF-1 to generate monocyte-derived macrophages. Groups were treated with ruxolitinib (rux), fedratinib (fed) or pacritinib (pac) at the concentrations shown and cell viability (as a percent of vehicle-treated controls) determined 48 hours later by MTT assay. (B, C) Monocyte-derived macrophages were treated with ruxolitinib (5 μM), fedratinib (5 μM), pacritinib (1 μM) or vehicle control (DMSO) and apoptosis determined by Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining 24 hours later. Values in C represent the percentage of total cells that were Annexin V−/PI− (n=3).