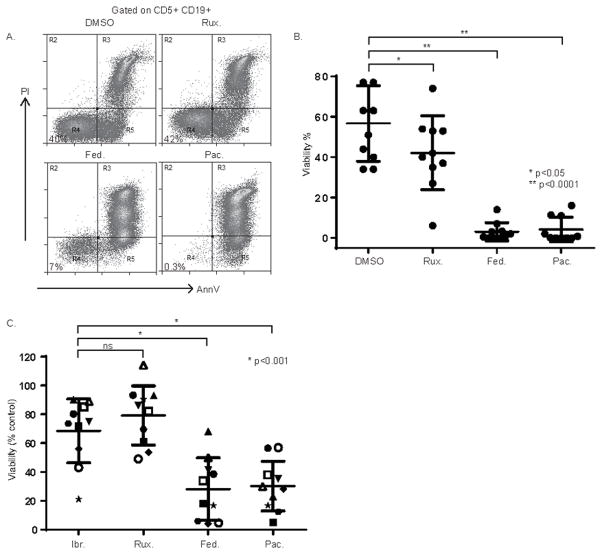
Figure 6.
Pacritinib impairs CLL B-cell survival. (A, B) NLC and CLL cocultures were generated from CLL patient PBMC (n=10) and were treated with ruxolitinib (5 μM), fedratinib (5 μM), pacritinib (1 μM) or vehicle control (DMSO). Viable CD5+CD19+ CLL cells were identified by Annexin V and PI staining (representative example is shown in A, and the data summarized in B). (C) In similarly performed experiments, CLL patient PBMC (n=10) were treated with ibrutinib (1 uM), ruxolitinib (5 μM), fedratinib (5 μM), pacritinib (1 μM) or vehicle control (DMSO) and viability of CD5+CD19+ CLL cells determined by Annexin V and PI staining. Viability was normalized to the paired DMSO control. High-risk CLL with a 17p deletion identified by FISH (n=3) are designated by an open symbol.