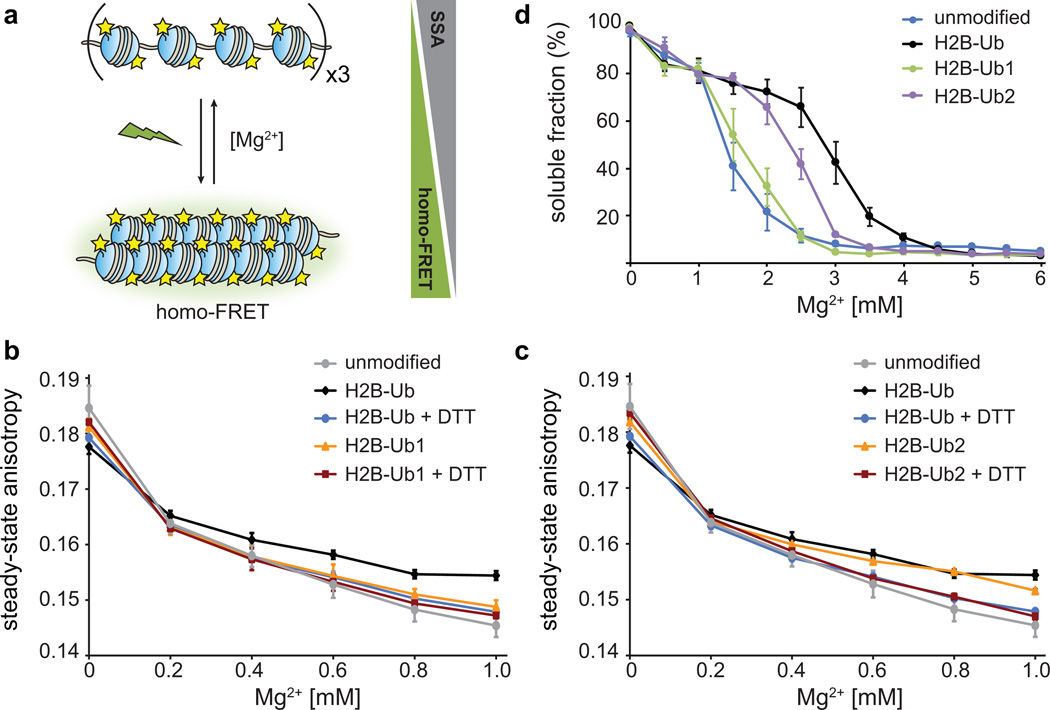
Figure 3.
Effect of ubiquitin mutations on intra- and inter-fiber compaction. (a) Homo-FRET based assay to detect intra-fiber compaction as a function of Mg2+. Each nucleosome contains fluorescein-labeled H2A, and upon compaction the fluorophores undergo homo-FRET detected as a decrease in the steady-state anisotropy. (b) Homo-FRET compaction assay of arrays containing H2B-Ub (black) and H2B-Ub1 (orange). Upon reduction of the asymmetric disulfide with dithiothreitol (DTT), the ubiquitin moiety is removed and the arrays compact similarly to unmodified nucleosome arrays (grey, blue and red). Error bars, s.d. (n = 3 independent array preparations) (c) Homo-FRET compaction assay of arrays containing H2B-Ub (black) and H2B-Ub2 (orange). Error bars, s.d. (n = 3 independent array preparations). (d) Oligomerization assay of unmodified nucleosome arrays (blue), and arrays containing H2B-Ub (black), H2B-Ub1 (green) and H2B-Ub2 (purple). The arrays were incubated with increasing amounts of Mg2+, the oligomers were removed by centrifugation, and the percentage of arrays remaining in solution was determined using SybrGold fluorescence. Error bars, s.e.m. (n = 3 – 6 independent array preparations). Ub1 designates ubiquitin with E16A and E18A mutations, and Ub2 contains I44A and F45A substitutions.