Fig. 5.
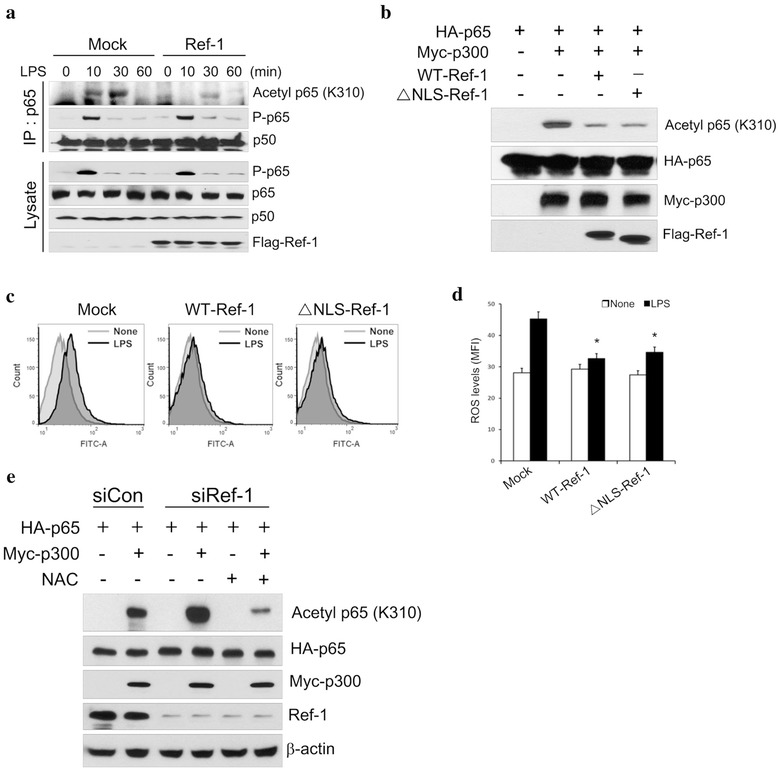
APE1/Ref-1 suppresses p300-mediated p65 acetylation via suppressing cellular ROS levels. a Primary cultured astrocytes were transiently transfected with wild-type- or ΔNLS-Ref-1, followed by LPS treatment for the times indicated. After immunoprecipitation with an anti-p65 antibody, the acetylation levels of p65 were detected by immunoblotting with an acetyl-lysine-specific antibody (top row). Co-immunoprecipitated p50 served as a positive control (top second row). Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with the antibodies indicated. b 293/TLR4/IL-1R cells were co-transfected with expression plasmids HA-p65 and Myc-p300 along with flag-tagged wild-type- or ΔNLS-Ref-1. Whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-acetyl-p65, HA, Myc, and flag antibodies. c Primary cultured astrocytes were transiently transfected with either wild-type- or ΔNLS-Ref-1, as described in (a), followed by LPS treatment for 10 min. ROS levels were measured with a flow cytometer (top panel) as described in the Methods. d Data were processed and quantified with FlowJo software. e 293/TLR4/IL-1R cells were transfected with either 100 pmol of scramble (control; siCon) or APE1/Ref-1 short interfering RNA (SiRef-1) along with the expression plasmids HA-p65 and Myc-p300 in the absence or presence of NAC (10 mM). Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies
