Figure 6.
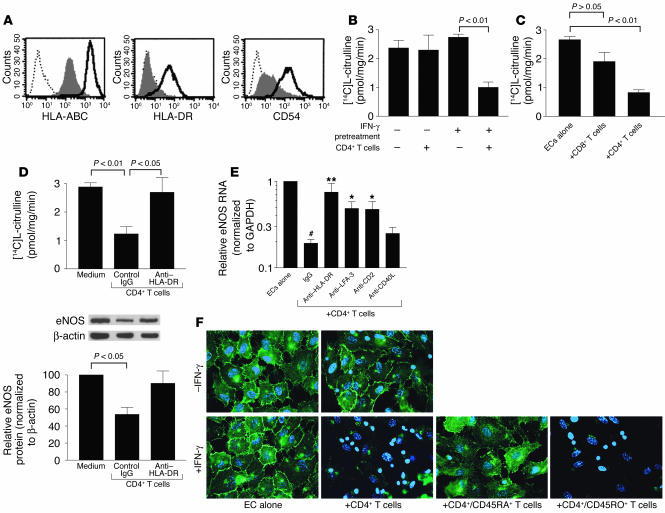
CD4+ memory T cells downregulate eNOS in class II MHC–positive ECs in vitro. (A) Flow cytometry of resting (shaded) or IFN-γ–pretreated (bold line) HUVECs immunostained for surface class I MHC (HLA-ABC), class II MHC (HLA-DR), and ICAM-1 (CD54). Dotted line, IgG1 control. (B) NOS activity of HUVECs, either untreated or pretreated with IFN-γ, after CD4+ T cell coculture. (C) NOS activity of IFN-γ–pretreated HUVECs after CD8+ or CD4+ T cell coculture. (D) NOS activity of IFN-γ–pretreated HUVECs after CD4+ T cell coculture with control or anti–HLA-DR mAb. Below: eNOS protein levels determined by Western blot and densitometry and normalized to levels of β-actin in arbitrary units. Data in A–D represent mean ± SEM from at least four experiments. (E) eNOS RNA levels in IFN-γ–pretreated HUVECs after CD4+ T cell coculture with control IgG, or inhibitory mAb against HLA-DR, LFA-3, CD2, and CD40L (CD154). Values were expressed relative to those of HUVECs alone. Isotype-matched IgG controls were pooled. Data represent mean ± SEM from five to eight experiments. #P < 0.001 vs. ECs alone; *P < 0.01 and **P < 0.001 vs. CD4+ T cell + IgG group. (F) Epifluorescence of eNOS cellular localization (green) with nuclei costaining (blue) in untreated or IFN-γ–pretreated HUVECs, cocultured with CD4+ T cells. IFN-γ–pretreated HUVECs were also cocultured with subsets of CD4+/CD45RA+ (naive) cells and CD4+/CD45RO+ (memory) cells. The smaller nuclei belong to T cells. Images are representative of three experiments. All cocultures were incubated for 3 days.