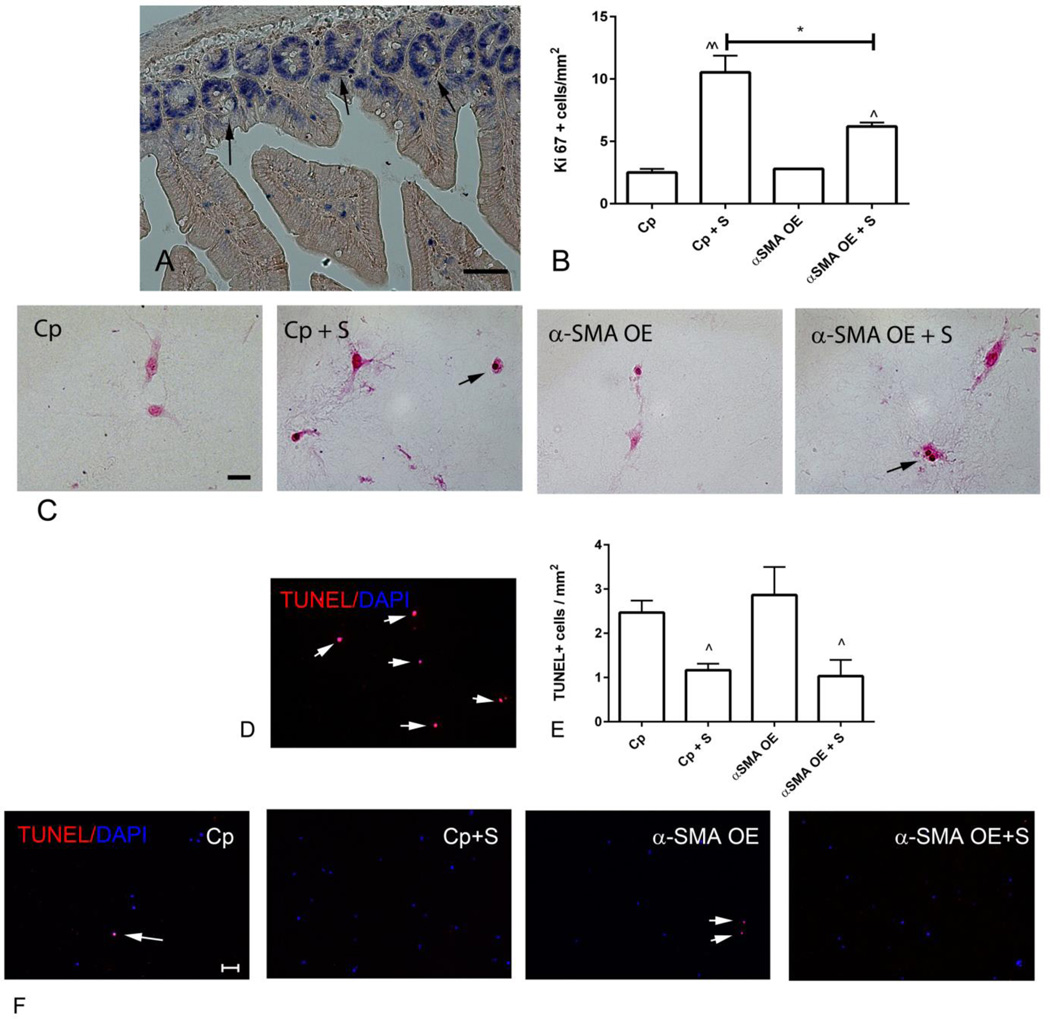
Figure 6.
α-SMA overexpression attenuates fibroblast proliferation, but does not affect apoptosis. A-C. Ki-67 immunohistochemistry was used to identify proliferating cells. A. Sections from the mouse bowel were used as a positive control, identifying proliferating epithelial cells in the base of intestinal crypts (arrows) (scalebar=50µm). B-C. Quantitative analysis of the density of Ki-67+ cells in pads showed that serum (S) increased the density of proliferating cells (C -arrows) (^p<0.05, ^^p<0.01 vs. control, *p<0.05; n=3/group). α-SMA overexpression (OE) did not affect the baseline density of proliferating cells (when compared with control-plasmid (Cp) cells), but attenuated serum-mediated proliferative activity (B- scalebar=20µm). D-F. TUNEL staining was used to identify apoptotic cells (scalebar=50µm). D. DNAse-treated sections served as a positive control (arrows). Small numbers of apoptotic cells were noted in control collagen pads (E, F - arrows). The density of apoptotic cells was reduced in serum-stimulated pads (^p<0.05 vs. corresponding unstimulated cells, n=3/group); however, α-SMA overexpression did not affect fibroblast apoptosis.