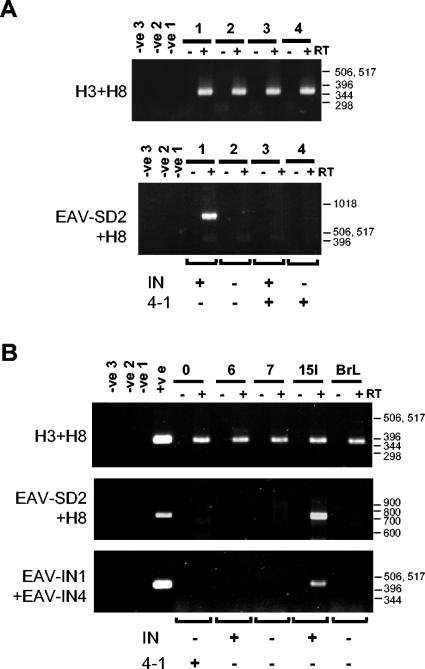
FIG. 2.
Expression of EAV-HP env subgenomic transcripts in CEF from a subset of EAV-HP proviruses with IN sequences and complete env genes. (A) RT-PCR detection of EAV-HP transcripts in primary CEF from four line 21 embryos. Total RNA was used for RT with Superscript RT II (+), with duplicate reactions set up without Superscript (−) to ensure detection of contaminating DNA. A general EAV-HP env PCR (H3+H8) was performed on the same RT reaction mixtures to verify for cDNA synthesis. Detection of the spliced env transcript was performed by nested PCR with primer EAV-SD2 and an anchor primer followed by EAV-SD2 with H8 (EAV-SD2+H8). Negative controls correspond to replicated reactions set up with water instead of RNA template for the RT (-ve1) or instead of DNA template for the first (-ve2) and second (-ve3) rounds of PCR. PCR typing of DNA from the same CEF samples for intact IN gene or the spliced env provirus (4-1) is indicated below the lower panel. (B) RT-PCR detection of env subgenomic transcripts in layer line 15I. RT-PCR was analyzed as described above on total RNA isolated from chicken embryos from five different layer lines, with DNA isolated from the same CEF for detection of the intact (IN) or the spliced (4-1) env gene. A third RT-PCR was performed on the same cDNA by use of primers EAV-IN1 and EAV-IN4 to detect genomic transcripts expressed from the EAV-HP proviruses whose pol-env junctions are preserved because the EAV-SD2 complementary region is deleted from the provirus of interest in line 6 chickens (Fig. 3). Negative controls were as described above, and positive controls were DNA samples from line 0 (top and middle panels) or line 15I (bottom panel) chickens. Positions of a 1-kb DNA ladder (Invitrogen) or 100-bp DNA ladder (Invitrogen) are indicated in base pairs.