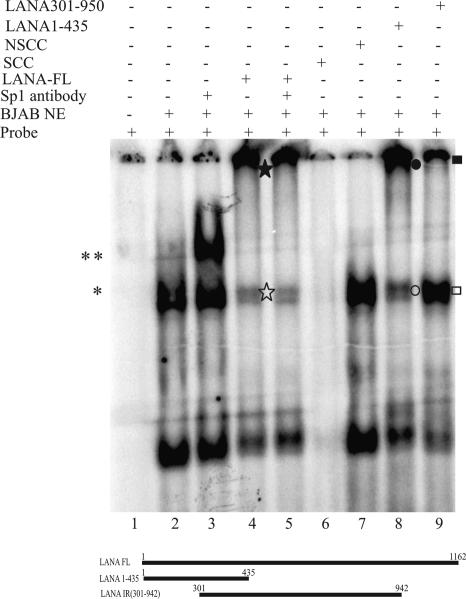
FIG. 8.
N terminus of LANA is sufficient for binding. A probe for the Sp1 binding sequence (GC box) spanning positions −119 to −98 of the hTERT promoter was labeled with [32P-α]dCTP and used for EMSAs in the presence of in vitro-transcribed and -translated LANA or different LANA mutants. Lanes 1 and 2, probe with and without BJAB nuclear extract (NE), respectively, showing activity due to Sp1 binding (*); lane 3, probe with BJAB nuclear extract and Sp1 mouse monoclonal IgG antibody, which supershifted the GC box probes (**); lane 4, in vitro-translated LANA, which abolished ([star]) the Sp1-specific shift, most likely due to the formation of a large complex that was unable to enter the gel ([starf]); lane 5, probe with Sp1 mouse monoclonal IgG along with in vitro-translated LANA and BJAB nuclear extract; lanes 6 and 7, probe with 200-fold molar excess of cold specific and nonspecific competitor, respectively. The LANA mutants were used for EMSAs, but only two mutants, LANA 1-435 (strong binding) and LANA 301-942 (very little or no binding), are shown in this figure. Lane 8, in vitro-translated N terminus of LANA (aa 1 to 435) along with the probe and BJAB nuclear extract, which abolished (○) the Sp1-specific band, forming a larger complex similar to that with full-length LANA (•); lane 9, LANA 301-942 did not show the elimination (□) of the Sp1-specific band and the accumulation of a larger complex (▪).