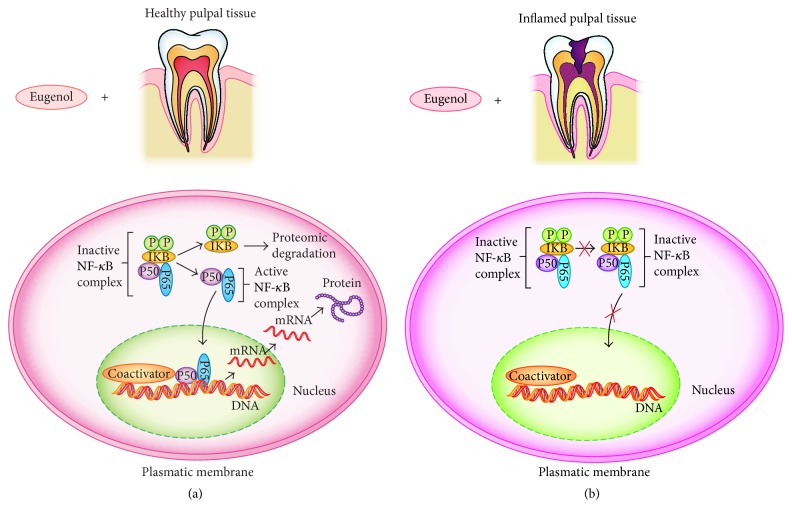
Figure 3.
A possible translocation of NF-κB for healthy pulp tissue (a) and inflamed pulpal tissue (b). (a) Healthy pulpal tissue. Eugenol allowed interaction with the IKB complex that mediates phosphorylation and degradation of inhibitor protein IKB, in turn activating the NF-κB transcription-B factor and translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus, where it participates in the activation of other genes involved in both inflammation and apoptosis. (b) Inflamed pulpal tissue. NF-κB expression is inhibited when there is preexisting inflammation because they do not carry out IKB phosphorylation inhibitor activities. P-phosphorylation; IKB-complex NF-κB inhibitor; P50-homodimer P50; P65-homodimer P65; NF-κB-nuclear factor kappa B.