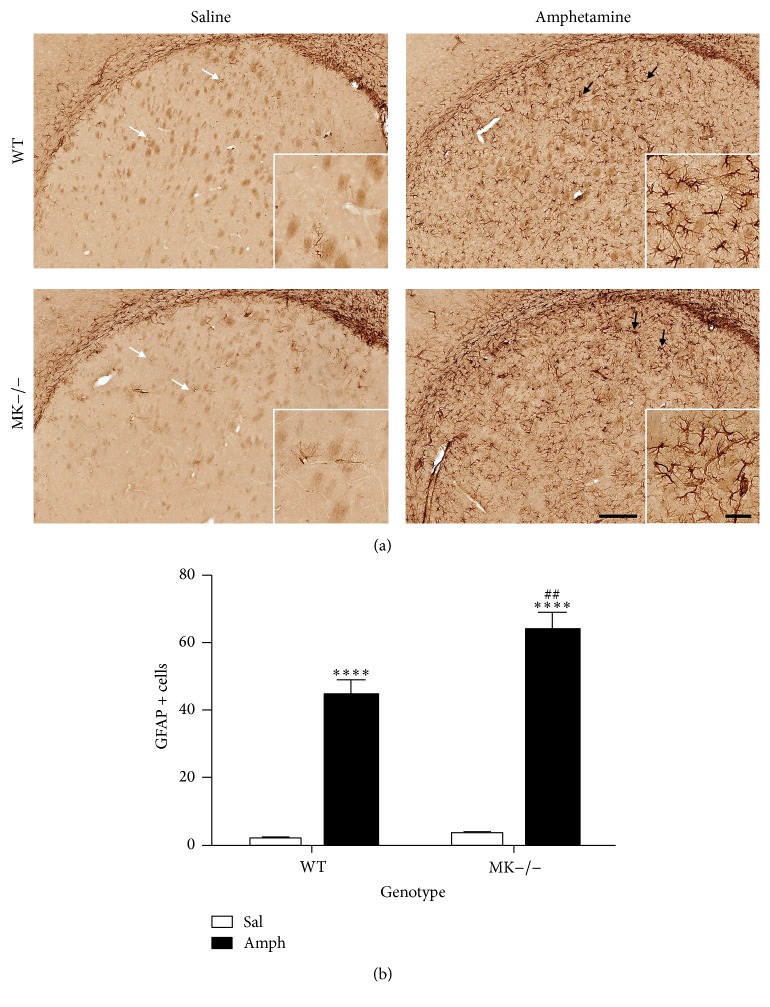
Figure 1.
Amphetamine induces astrocytosis in the striatum of WT and MK−/− mice. (a) Photomicrographs are from GFAP-immunostained striatal sections of saline- (Sal-) or amphetamine- (Amph-) treated animals. Amphetamine induced reactive astrocytes characterized by larger densely stained bodies with longer and extensive processes (black arrows) compared to saline-treated mice (white arrows). (b) The graph represents quantification of data (mean ± SEM) obtained from the counts of GFAP-positive cells in standardized areas of the striatum. Significant effects of the genotype (F (1,16) = 8.051, P = 0.01), the treatment (F (1,16) = 200.3, P < 0.0001), and genotype by treatment variant interaction (F (1,16) = 5.896, P = 0.03) were found. ∗∗∗∗ P < 0.0001 versus Sal. ## P < 0.01 versus WT. Scale bar = 200 μm. Magnified inset = 50 μm.