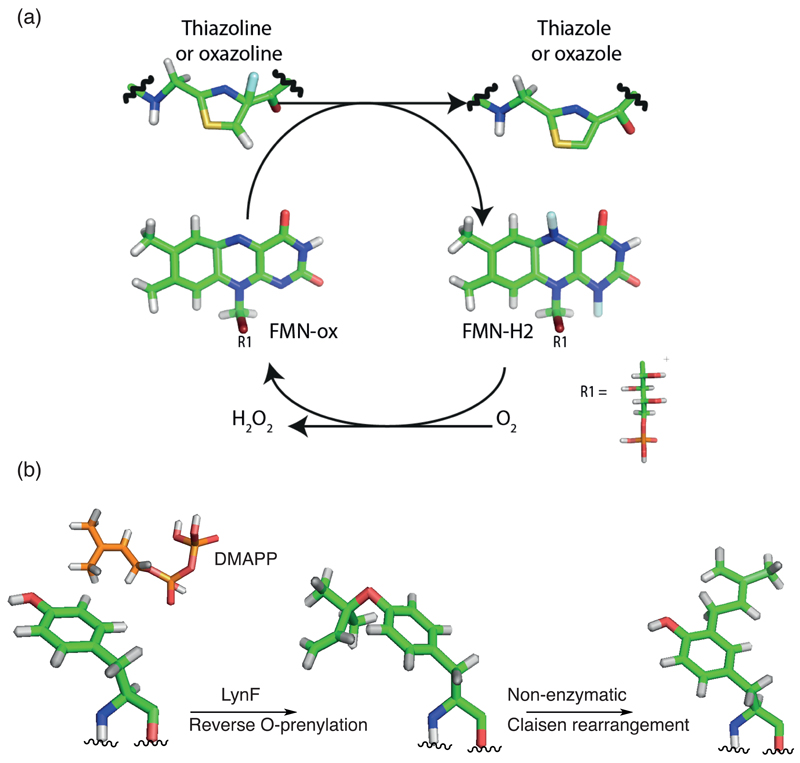
Figure 4. Oxidation and prenylation.
(a) Simplified reaction scheme for the reaction catalyzed by the thiazoline and/or oxazoline oxidase protein. During the course of the reactions, oxidized flavine mononucleotide (FMN-ox) receives either one hydride and one proton or 2 single electrons and 2 protons from the thiazoline or oxazoline, generating reduced flavine mononucleotide (FMN-red). The exact mechanism remains to be determined. The catalytic competent FMN-ox is produced by reaction with oxygen to release hydrogen peroxide. (b) Tyrosine O- and C-prenylation as examples of prenylation in cyanobactins. The hydroxyl group on tyrosine is reverse O-prenylated by LynF using DMAPP (Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate). The product can subsequently undergo non-enzymatic Claisen rearrangement to give C-prenylated tyrosine.