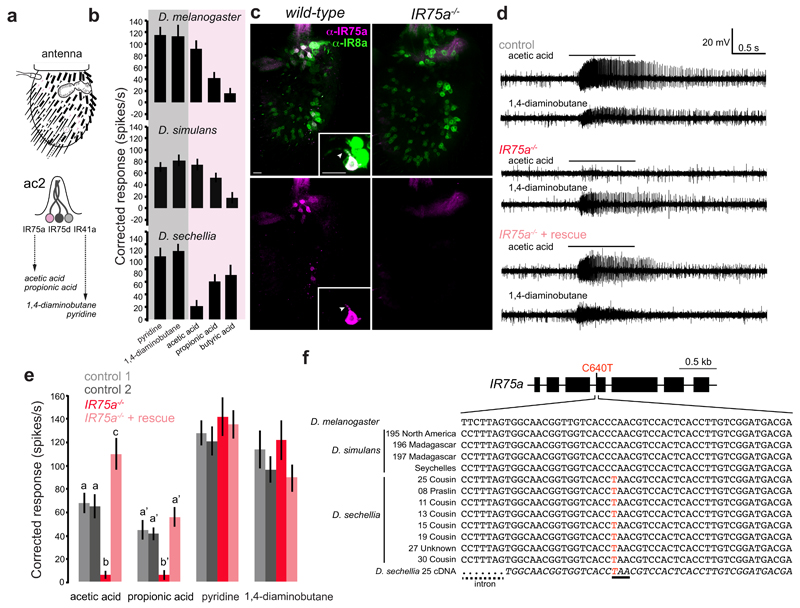
Fig. 1. Ir75a encodes an acetic acid receptor in D. melanogaster, and is a transcribed pseudogene in D. sechellia.
a, Top: schematic of the third antennal segment covered with porous olfactory sensilla of various morphological classes. Bottom: schematic of the ac2 sensillum class, which houses three olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) that express different Ir genes.
b, Electrophysiological responses in ac2 sensilla to the indicated odours (mean±SEM; mixed genders) in D. melanogaster30 (n=9), D. simulans31 (n=9) and D. sechellia31 (n=8). The shading on the histograms distinguishes two broad chemical classes of odours (magenta [acids], grey [amines]).
c, Immunostaining with ?anti-IR75a (magenta) and anti-IR8a (green) antibodies on antennae of wild-type (left) or Ir75a mutant (Ir75aMB00253, right) animals. The inset shows the colocalisation of IR75a and IR8a in the OSN soma and dendritic compartment (arrowhead). Scale bars = 10 μm.
d, Representative traces of extracellular recordings of neuronal responses to the indicated stimuli in ac2 sensilla in control (Ir75a-Gal4,Ir75aMB00253/+), Ir75a hemizygous mutant (Ir75aMB00253/Df(3L)BSC415) and Ir75a rescue (UAS-DmelIr75a;Ir75a-Gal4,Ir75aMB00253/Df(3L)BSC415) animals. Bars above the traces mark 1 s stimulus time.
e, Quantification of solvent-corrected responses in (d) (mean±SEM; mixed genders). Genotypes: control 1 (Df(3L)BSC415/+, n=12), control 2 (Ir75a-Gal4,Ir75aMB00253/+, n=11), Ir75a hemizygous mutant (Ir75a-Gal4,Ir75aMB00253/Df(3L)BSC415, n=12), Ir75a rescue (UAS-DmelIr75a;Ir75a-Gal4, Ir75aMB00253/Df(3L)BSC415, n=13). Bars labelled with different letters are significantly different (Source Data & Methods). For odours with unlabelled bars, no significant differences were found across genotypes.
f, Top: gene model of Ir75a indicating the position of the C640T nucleotide change in the D. sechellia orthologue. Bottom: Genomic sequence spanning this nucleotide position in D. melanogaster and several geographically-distributed D. simulans and D. sechellia strains (Methods). The bottom italicised sequence is of the D. sechellia cDNA. The D. sechellia C640T substitution (highlighted in red) creates a premature termination codon (underlined).