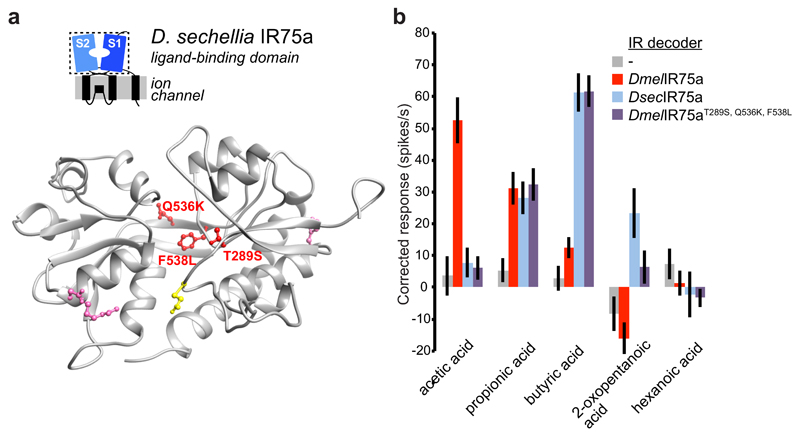
Fig. 4. Molecular basis of the functional divergence of D. sechellia Ir75a.
a, Protein homology model of the LBD of DsecIR75a (Methods). The side chains of the residues that are different in D. sechellia IR75a compared with D. simulans and D. melanogaster IR75a are represented in pink, and the subset of these mutated in this study are shown in red. The location of the residue putatively encoded by the PTC is shown in yellow.
b, Quantification of odour-evoked responses in empty IR decoder neurons (Ir84aGal4, n=5-6) or the decoder neurons expressing DmelIR75a (n=9), DsecIR75a (n=8-9) or the DmelIR75aT289S,Q536K,F538L mutant (n=14) (genotypes: UAS-DxxxIr75axxx;Ir84aGal4) (mean±SEM;, mixed genders); experiments for all transgenes were performed in parallel. Responses to each odour of DsecIR75a and DmelIR75aT289S,Q536K,F538L are statistically indistinguishable (Wilcoxon sum-rank test).