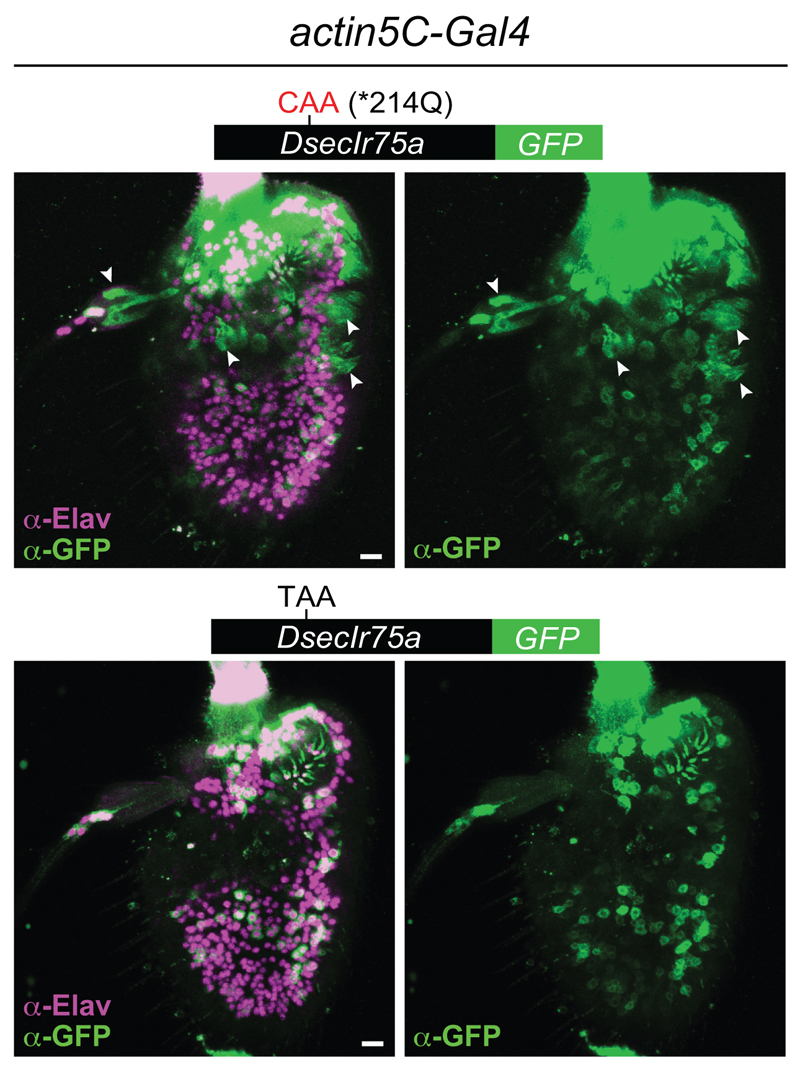
Extended Data Fig. 2. Tissue-specificity of translational readthrough of the D. sechellia Ir75a PTC.
Immunofluorescence with anti-GFP (green) and the neuron nuclear marker anti-Elav (magenta) on whole-mount D. melanogaster antennae in which actin5C-Gal4 drives broad expression of DsecIR75a*214Q:GFP (UAS-DsecIr75a*214Q:GFP/act5C-Gal4) or DsecIR75a:GFP (UAS-DsecIr75a:GFP/act5C-Gal4). Arrowheads indicate GFP-expressing, Elav-negative, non-neuronal cells that were observed in 6/6 antennae expressing the control transgene lacking the PTC, and in 0/6 antenna expressing the PTC-containing transgene. Note that the neuronal GFP signal of both transgenes is heterogeneous across the antenna, possibly because of variable strength of driver expression and/or instability of the GFP-tagged receptors in heterologous neurons. Scale bars = 10 µm.