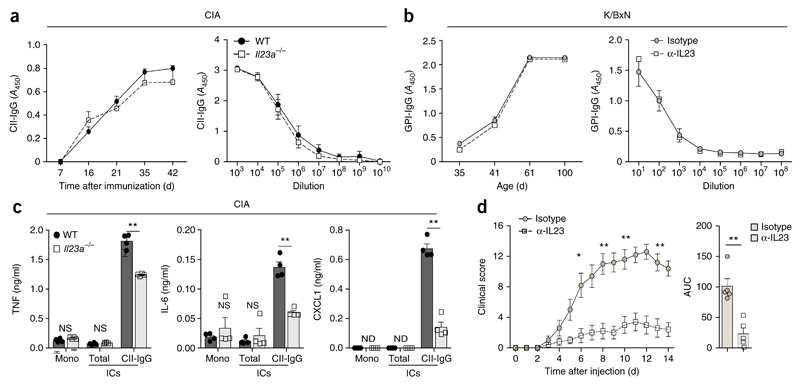
Figure 2. IL-23 promotes the inflammatory activity of autoreactive IgG.
(a,b) Concentration (left) and titers (right) of CII-specific IgG (CII-IgG) during CIA in wild-type and Il23a−/− mice (n ≥ 3 per genotype) (a) and of IgG directed against GPI (GPI-IgG) in K/BxN mice that received neutralizing antibody to IL-23p19 or isotype-matched control antibody (n ≥ 3 mice per group) (b); results are presented as absorbance at 450 nm (A450). (c) ELISA of cytokines TNF, IL-6 and CXCL1 in supernatants of wild-type BMDCs incubated for 24 h with monomeric IgG (Mono) or ICs consisting of total (heat-aggregated) IgG (Total) or CII-specific IgG (CII-IgG), generated from IgG isolated from the serum of wild-type or Il23a−/− mice (n = 4 per group) on day 50 after the induction of CIA. (d) Clinical arthritis scores of wild-type mice (n = 5 per group) after transfer of serum from K/BxN mice that had received neutralizing antibody to IL-23p19 or isotype-matched control antibody. Each symbol (c, and d, right) represents an individual biological replicate (c) or mouse (d, right). ND, not detectable. P = 0.2 (a) or P = 0.48 (b); NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P ≤ 0.01 and **P ≤ 0.001 (P ≤ 0.0002 in c) (Student’s t test). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments (error bars, s.e.m.).