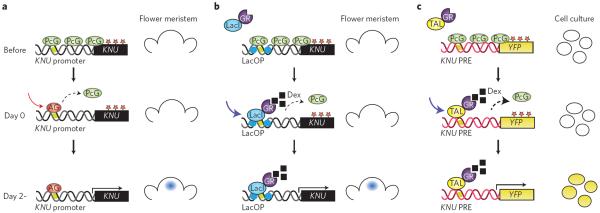
Figure 4. A synthetic epigenetic timer for gene expression.
a, The endogenous timer. During flower development, KNU is covered with H3K27me2 repressive marks (red stars). The PcG complex maintains such marks (top). Binding of AG to the KNU promoter elements triggers eviction of PcG (middle). After two days, cell-division-dependent loss of repressive histone marks facilitates KNU gene expression in the flower meristem (bottom; right). b, A partially synthetic timer. On dexamethasone (Dex) treatment, LacI–GR, a synthetic DNA-binding protein consisting of the LacI DNA-binding domain fused to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), can trigger the eviction of the PcG complex from the KNU promoter region that contains Lac operator (LacOp) sequences (middle). This leads to KNU gene expression after two days, thus mimicking the AG action (bottom, right). c, A completely synthetic timer. YFP driven by an unrelated promoter can be silenced with repressive histone marks (asterisks) if a Polycomb response element from KNU (KNU PRE) is inserted (top). A synthetic DNA-binding protein consisting of GR fused with TAL that is designed to bind near the AG-binding site, TAL–GR, can trigger the eviction of PcG (middle). This leads to YFP reporter gene expression in cultured cells (bottom; right).