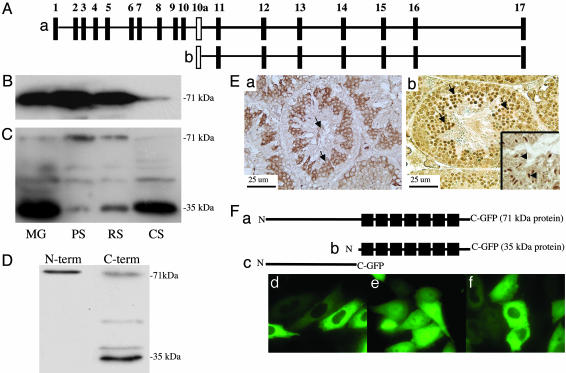
Fig. 1.
Deduced structure of the Pf20 gene and analysis of the two PF20 proteins expressed during spermatogenesis. (A) Map of the Pf20 gene. (a) Exons encoding the 2.5-kb transcript. (b) Exons encoding the 1.4-kb transcript. (B) Western blot analysis of germ cell extracts (MG, mixed germ cells; PS, pachytene spermatocytes; RS, round spermatids; CS, condensing spermatids) with anti-PF20 antibody to the N-terminal domain. (C) Western blot analysis of germ cell extracts with anti-PF20 antibody to the C-terminal domain. The C-terminal antibody weakly reacts with a protein of 50 kDa, which may be a fragment of the larger PF20 protein. (D) Western analysis of epididymal sperm with anti-N- and anti-C-terminal antibodies showing the presence of both PF20 isoforms. The 38-kDa PF20 band detected in this blot likely represents a phosphorylated form of 35-kDa PF20. (E) Immunochemistry of normal testis with anti-PF20 antibodies to the N (a) and C(b) termini. The N-terminal antibody stains the cytoplasm of maturing germ cells and the flagella of sperm. The C terminus antibody similarly stains the cytoplasm but shows much more intense staining of the nuclei of round (arrows) and condensing (Inset, arrows) spermatids. (F) Map of GFP fusion proteins (a–c) and CHO cells transfected with plasmids expressing the 71-(d) and 35-(e) kDa and N-terminal (f) GFP fusion proteins showing cytoplasmic localization of the 71-kDa and N-terminal fusion proteins and cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of the 35-kDa fusion protein.