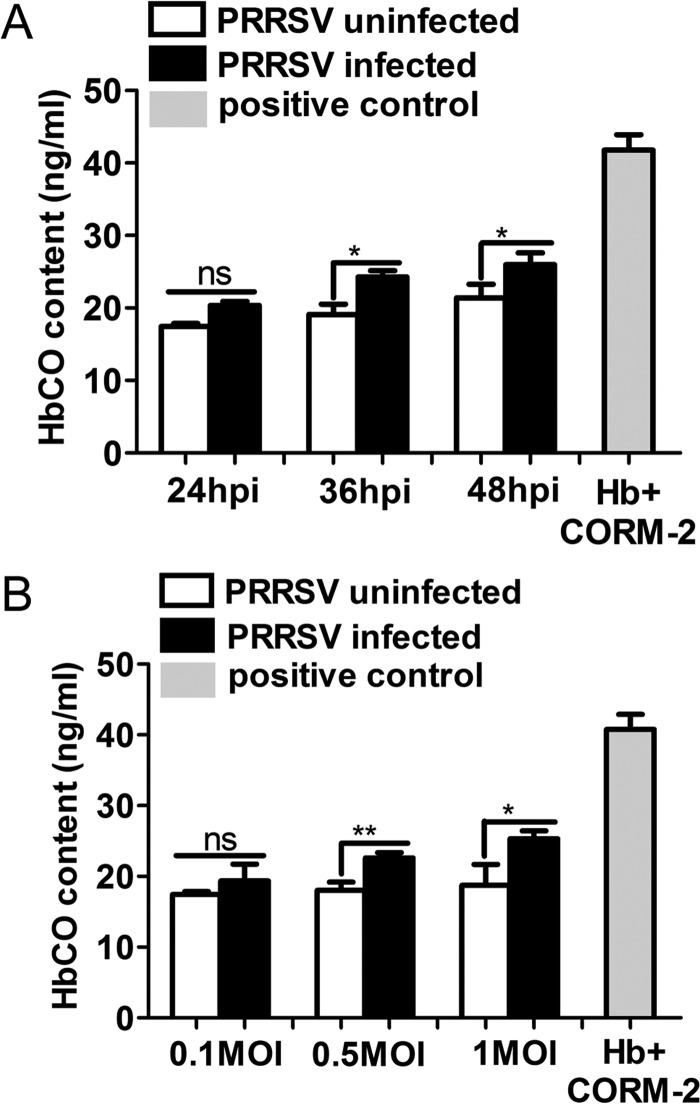
FIG 1.
PRRSV infection promotes CO production. (A) MARC-145 cells infected with PRRSV at an MOI of 0.1 were treated with Hb (50 μg/ml) from 1 hpi onward. At 24, 36, and 48 hpi, cell culture supernatants were harvested for HbCO detection by ELISA to quantify HbCO levels as a measure of CO. MARC-145 cells mock infected with PRRSV were included as a control. (B) MARC-145 cells were infected with different doses of PRRSV (MOIs, 0.1, 0.5, and 1), and then the cells were incubated with 50 μg/ml Hb for 24 h. The HbCO contents in culture supernatants were determined by ELISA as a measure of CO. Uninfected MARC-145 cells were included in the analysis as a control. Hb (50 μg/ml) was coincubated with CORM-2 (150 μM) for 1 h, and then the contents of HbCO were detected simultaneously as a positive control (A and B). Data are expressed as the means ± standard deviations (SD) of the results of three independent experiments. P values were calculated using Student's t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, not significant. White columns represent PRRSV-mock-infected MARC-145 cells, black columns represent PRRSV-infected MARC-145 cells, and gray columns represent the positive control.