FIG 1.
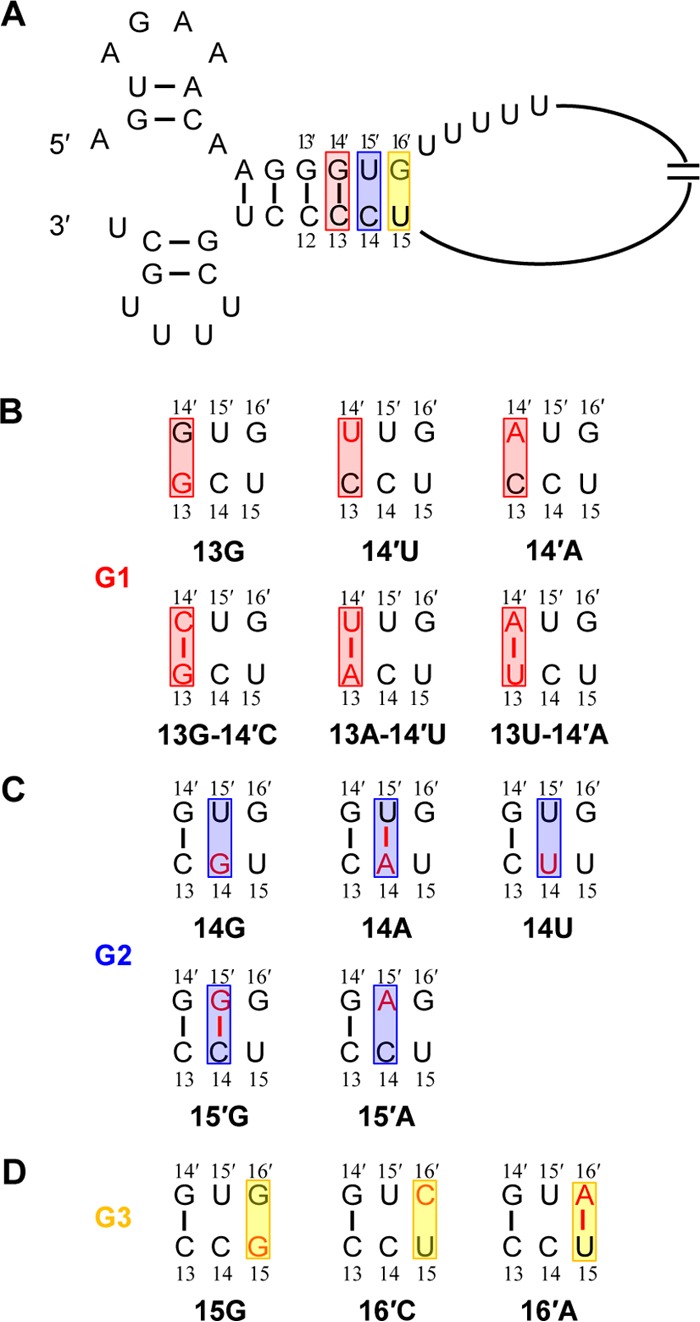
The HA segment-specific nucleotides in the extended duplex region of the viral RNA promoter and the mutagenesis strategies used in this study. (A) Representation of HA segment-specific nucleotides next to the viral RNA promoter in the corkscrew configuration. The common stretch of uridine residues is also shown. The extended duplex region potentially formed by the HA segment-specific nucleotides is highlighted with red, blue, and yellow rectangles at the 13-14′, 14-15′, and 15-16′, positions, respectively. Base pairs are indicated with a connecting line. (B to D) Mutations introduced at the HA segment-specific nucleotide sites. Mutations made at the 3′-end position 13 and/or 5′-end position 14′ belong to the G1 mutants. Mutations made at the 3′-end position 14 and/or 5′-end position 15′ belong to the G2 mutants. Mutations made at 3′-end position 15 and/or 5′-end position 16′ belong to the G3 mutants.
