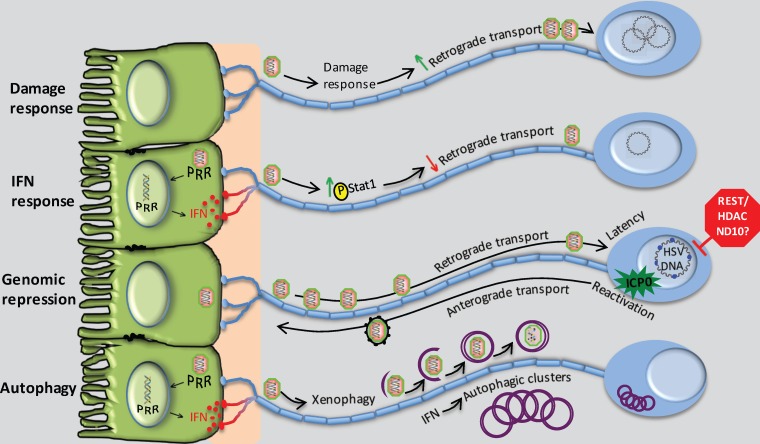
FIG 1.
Intrinsic and innate pathways that modulate alphaherpesvirus infection in peripheral neurons. (From the top) The damage response of neurons may be co-opted by the virus to promote the efficiency of retrograde transport to the cell body. Interferon synthesized by, for example, infected epithelial cells increases levels of phosphorylation of local axonal Stat1, serving to reduce retrograde transport, a response that may be countered by HSV γ34.5. Genomic repression of HSV mediated by intrinsic neuronal factors promotes the establishment and maintenance of latency, which is countered through expression of ICP0. Autophagy induced through IFN-dependent signaling leads to xenophagic clearance of HSV and formation of clusters of autophagosomes that may regulate the latency process.