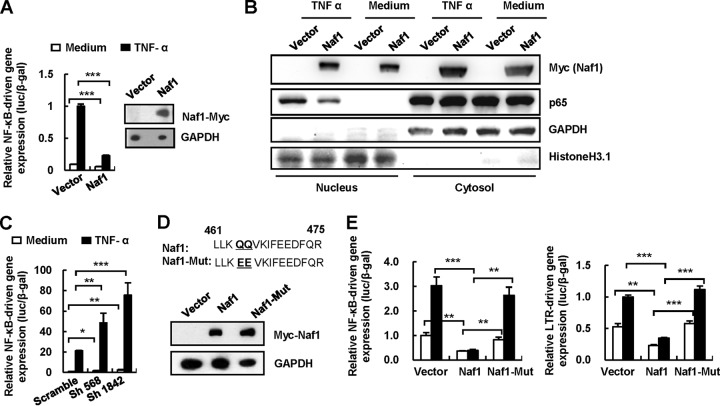
FIG 2.
Naf1 suppresses NF-κB-dependent HIV-1 LTR-driven gene expression. (A) Naf1 overexpression inhibits NF-κB activation. The myc-tagged plasmid pCMV-Tag 3B/Naf1 or vector and an NF-κB reporter plasmid were cotransfected into HEK293T cells, and a β-Gal-expressing vector was used to normalize the transfection efficiency. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were treated with or without TNF-α for an additional 24 h, and then cells were harvested and reporter gene expression assessed. (B) Naf1 blocks NF-κB p65 nuclear import. HEK293T cells were transfected with myc-tagged pCMV-Tag 3B/Naf1 or vector for 24 h, and then cells were stimulated with or without TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 30 min. The cytoplasmic and nuclear protein extracts were then isolated, and NF-κB p65 was detected by immunoblotting. The histone H3.1 and GAPDH proteins were used to validate the nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts, respectively, and one blot representative of three repeats is shown. (C) Naf1 knockdown significantly increases TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation. The endogenous Naf1 in HEK293T cells was knocked down by use of Naf1-specific shRNA. Cells were transfected with an NF-κB reporter plasmid, and reporter gene expression was detected as described above. (D and E) Inhibition of NF-κB activation and HIV-1 LTR-promoted gene expression by a Naf1 mutant. A Naf1 mutant was constructed and its expression confirmed by immunoblotting (D), and the inhibition of NF-κB activation and HIV-1 LTR-promoted gene expression by mutant (Mut) and wild-type Naf1 was detected as described above (E). Data are presented as means ± SD. Results in panels A, C, and E are representative of at least four independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (unpaired t test).