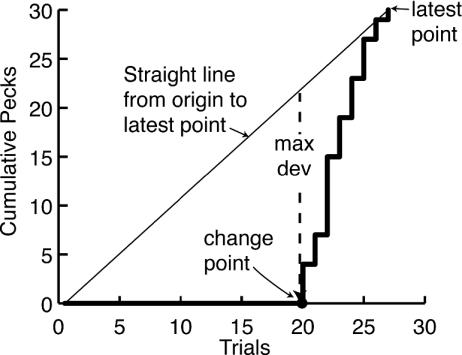
Fig. 5.
In this illustration, the algorithm for finding change points is applied to the cumulative record as of Trial 27. (In practice, it is applied iteratively to each successive point in the cumulative record.) In this record, there were no pecks until Trial 20, where pecking began. The slanted dashed line is a straight line drawn between the origin and the cumulative record at end of Trial 27. The cumulative record deviates maximally from this straight line between Trials 19 and 20, so that is the putative change point. It divides the record up to Trial 27 into two portions: Trials 1–19 and Trials 20–27. If the change point is accepted as valid, then the algorithm begins over again, with the pecks on Trial 20 as the first datum.