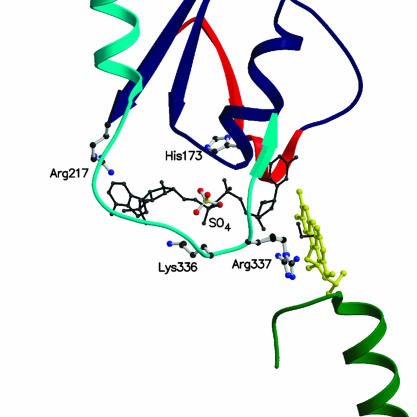
Fig. 6.
Close-up view of the NADP-binding site at the domain interface. The FAD cofactor is shown in yellow. Ribbons are colored as in Fig. 3. The picture shows the position of residues that have been shown to be crucial for catalysis and/or NADPH binding. A NADPH molecule is shown modeled in the conformation observed in topologically similar enzymes (black). The image was generated by superimposing the NADP-binding domain of human glutathione reductase in complex with NADPH (29) to the corresponding domain of PAMO. The resulting position of the NADPH molecule bound to glutathione reductase is depicted. As a reference, a model for the peroxide adduct is shown in black. The adduct has been modeled based on the three-dimensional structure of 4a,5-epoxyethano-3-methyl-4a,5-dihydrolumiflavin (38).