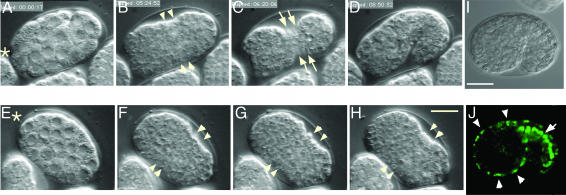
Fig. 2.
paf-2(tj12) mutant fails to elongate. (A–H) Nomarski micrographs of wild-type (A–D) and paf-2(tj12) (E–H) by four-dimensional microscopy. (A–D) A wild-type embryo is enclosed by an epidermal sheet (B and C, ventral view) and subsequently elongates (D, lateral view, dorsal up). The ventral epidermal cells are visible on the ventral surface (C, arrows). (E–H) A paf-2(tj12) embryo appears to be normal during the cell proliferation stage (E and F), but does not elongate (G and H, see text). The anterior of the worm is indicated by asterisks. (I and J) paf-2::GFP expression in embryos (lateral view, dorsal is up). Nomarski micrographs (I) and corresponding paf-2::GFP expression (J). paf-2 reporter gene constructs are expressed in epidermal cells (J, arrowheads) and intestinal cells (J, arrow) at the beginning of elongation. Anterior is to the left. (Bar, 10 μm.)