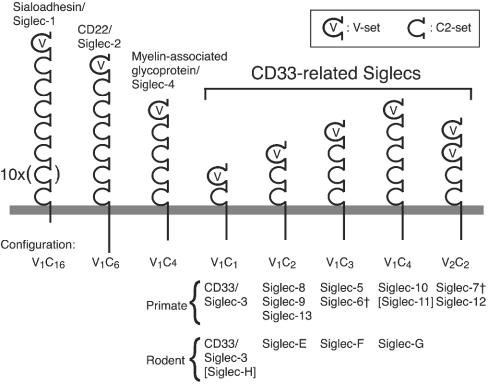
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of Siglecs in primates and rodents. Siglecs have one V-set domain (a domain similar to Ig's variable region) and 1–16 C2-set domains (domains similar to Ig's constant region), followed by transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Genes for Sialoadhesin/Siglec-1, CD22/Siglec-2, and myelin-associated glycoprotein/Siglec-4 are located outside of the Siglec gene cluster in both primates and rodents. Clear orthologs have been established for each of these genes between human and mouse. Most of the genes for CD33rSiglec subfamily are in the Siglec cluster described here, with the exception of primate Siglec-11 and rodent Siglec-H, whose genes are outside of the gene cluster (indicated with square brackets). CD33rSiglecs are further classified into five subgroups (V1C1, V1C2, V1C3, V1C4, and V2C2), based on the number of V- and C2-set Ig-like domains. The basic configuration of the V2C2 subgroup (Siglec-7 and 12/XII) is V1 + V1C2, and the V1C2 part is highly similar to other Siglecs with V1C2 configuration and thus can be considered a part of the V1C2 subgroup. Although the primate SIGLEC6 gene has V1C3 configuration similar to that of SIGLEC5, the exon coding for a potential third C2-set domain is inactivated. Similarly, the primate SIGLEC7 gene has the exon coding for a potential second V-set domain inactivated. These are indicated with †.