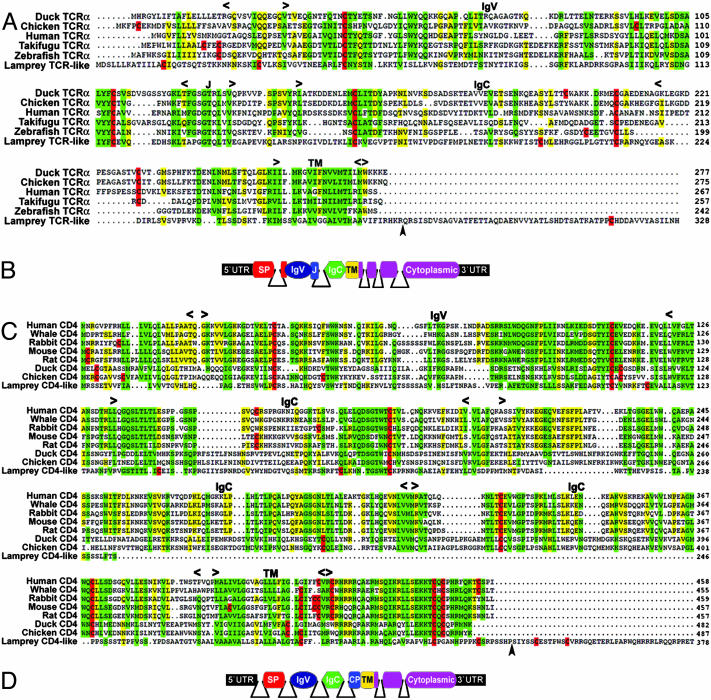
Fig. 1.
Multiple alignment of the lamprey TCR-like and CD4-like molecules with related vertebrate lymphocyte receptors. (A and C) Jawed vertebrate TCRα and CD4 molecules. Approximate location of Ig and transmembrane (TM) domains as well as the location of the J region in TCRs are indicated. Arrowheads indicate the positions of intron 4 in the lamprey TCR-like and intron 6 in the CD4-like. Cysteine residues are highlighted in red. Green, ≥80% identity and similarity; yellow, 60-79% identity/similarity. Amino acid similarity groups are as follows: acidic, D and E; aromatic, F, W, and Y; basic, H, K, and R; hydrophobic, A, I, L, M, and V; polar, N, Q, S, and T; and ungrouped, G and P. (B and D) Stick models of exons and introns in the TCR-like and CD4-like genes. The position of introns was determined by sequencing genomic clones and are indicated by solid lines. SP, signal peptide; CP, connecting peptide. GenBank accession nos. for the sequences shown in A are as follows: duck, AN3311A9; chicken, AAC98541; human, AAC14929; takifugu (Takifugu rubripes), AAF97794; zebrafish (Danio rerio), AAL23935; and lamprey TCR-like, AY686861. GenBank accession nos. for the sequences shown in C are as follows: human, NP_000607; white whale (Delphinapterus leucas), AAD23738; rabbit, P46630; mouse, NP_038516; rat, NP_036837; duck, AAK59279; chicken, NP_989980; and lamprey CD4-like, AY686862.