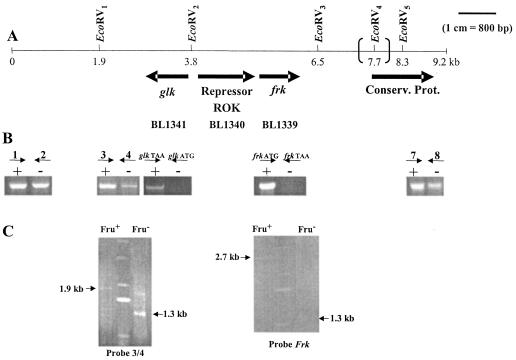
FIG. 6.
Genetic context of frk locus in two B. longum strains (NCC2705 and DJ010A) and genotype analysis of the fructose-negative strain DSM20219. (A) EcoRV restriction map of a 9.2-kb fragment of the chromosome of B. longum NCC2705 surrounding the frk locus. The additional 1,119-bp noncoding sequence separating frk from the downstream ORF on the DJO10A genome and the additional EcoRV4 site are indicated with large parentheses. (B) Analysis by agarose gel electrophoresis of amplicons generated by PCRs performed with fructose-positive A10C (+) and fructose-negative DSM20219 (−) genomic DNAs. The following sets of primers were designed to amplify DNA fragments located around the frk locus: 1-2 (861 bp), 3-4 (768 bp), glkATG-glkTAA (908 bp), frkATG-frkTAA (894 bp), and 7-8 (784 bp). (C) (Left) Southern blot of EcoRV-digested DNA from the A10C (Fru+) and DSM20219 (Fru−) strains hybridized with probes 3 and 4. (Right) Southern blot of EcoRV-digested DNA from the A10C (Fru+) and DSM20219 (Fru−) strains hybridized with the frk probe. Arrows indicate the specific bands detected with probes amplified from B. longum A10C genomic DNA. On both gels, the central lane corresponds to DNA ladder X (Roche).