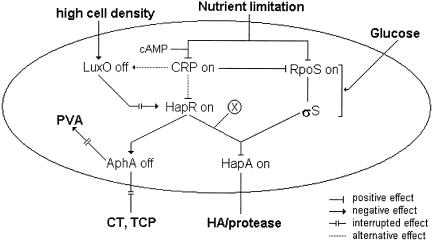
FIG. 8.
Regulatory interactions involved in hapA transcription regulation. The hapA gene is transcribed in response to two concurrent environmental signals: high cell density and nutrient limitation. Nutrient limitation leads to entry of bacteria into the stationary phase, with enhanced transcription of rpoS and high levels of σS. At high cell density in the stationary phase, HapR is expressed and, in combination with an unidentified factor (X) and σS, activates the transcription of hapA. Glucose represses hapA transcription by inducing cells to resume exponential growth, blocking the pathway to accumulation of σS. The cAMP-CRP complex enhances the transcription of hapA by positively influencing the transcription of rpoS and hapR. CRP could increase HapR levels by acting on luxO or hapR. HapR represses the expression of AphA, required for the production of CT and TCP. In the absence of AphA, pva, encoding penicillin V amidase, is expressed.