Figure 7.
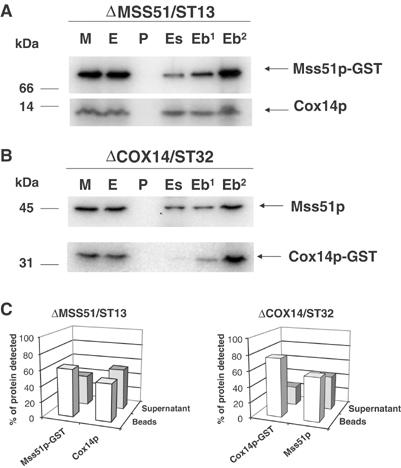
Cox14p interacts with Mss51p. (A) Mitochondria (M) from an mss51 null mutant with a chromosomally integrated plasmid expressing Mss51p-GST fusion protein (ΔMSS51/ST13) were extracted with 1% lauryl maltoside, 1 M KCl, and 1 mM PMSF. The pellet (P) after centrifugation at 50 000 gav for 30 min was suspended in the starting volume of buffer and the extract (E) was mixed and incubated for 4 h at 4°C with glutathione–Sepharose. The supernatants (Es) from the beads were collected and the beads (Eb) were washed three times with PBS. The different fractions adjusted for volume were separated by SDS–PAGE. The lane labeled (Eb2) was loaded with two times the amount of beads. Cox14p and Mss51p-GST were detected by Western blot analysis using specific antibodies against each protein. The proteins were visualized by a secondary reaction with [125I]protein A and the radiolabeled bands were detected with a PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics). (B) Same as (A) except that the mitochondria were prepared from a cox14 null mutant with an integrated plasmid expressing a Cox14p-GST fusion protein (ΔCOX14/ST32). (C) The bands shown in (A, B) were quantified with the PhosphorImager. The open bars represent the percentage of the corresponding protein bound to the beads, and the filled bars represent the percentage of unbound protein recovered in the supernatant fraction.
