Figure 10.
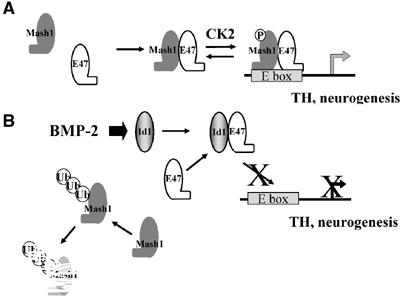
Model of mechanisms of repression of Mash1 by BMP-2/Id1. (A) In differentiating neurogenic precursors, Mash1 heterodimerizes with E proteins, which promotes phosphorylation of Mash1 on Ser152, increasing further heterodimer interaction. (B) Activation of the BMP signaling pathway leads to increased levels of Id proteins. Id proteins sequester E proteins away from Mash1, which leads not only to transcriptionally inactive complexes but also enhances degradation of Mash1 monomers.
