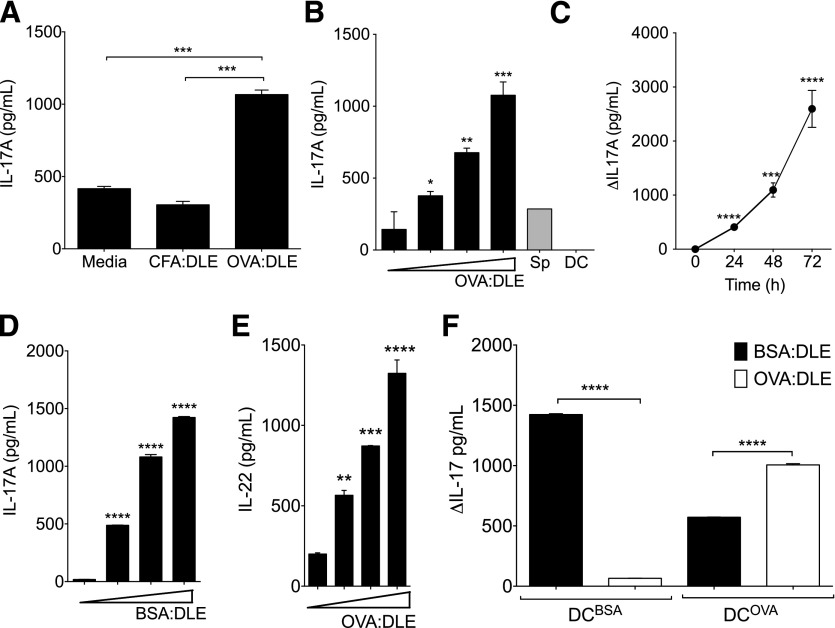
Figure 2. DLE stimulates antigen-specific IL-17 production from antigen-naïve splenocytes.
Whole splenocytes (2e6) were harvested from OVA-naïve mice and cocultured with DCOVA (4e5) in 1 ml total media. (A) 1e5 ceq of DLE from mice immunized with CFA and OVA (OVA:DLE) or CFA alone (CFA:DLE) was added to the culture media. Supernatants were harvested after 72 h and analyzed for IL-17A. (B) Dose-response curve for OVA:DLE (0, 1e4, 1e5, and 1e6 ceq) added to cocultures (black bars) or splenocytes (Sp) or DC alone (gray bars; 1e6 ceq). IL-17A measured after 72 h of incubation. (C) 1e6 ceq of OVA:DLE added to cocultures. IL-17A measured at 24 h increments and depicted as change (Δ) versus time-matched media control. (D) Titrated doses (0, 1e4, 1e5, and 1e6 ceq) of DLE derived from mice immunized with CFA and BSA (BSA:DLE) were added to cocultures of BSA-naïve splenocytes and DCBSA. Supernatant IL-17A was measured after 72 h. (E) IL-22 induced from 1e4–1e6 ceq OVA:DLE added to cocultures as in B. (F) 1e6 antigen-naïve splenocytes were cocultured with 4e5 DCBSA or DCOVA in 1 ml total media. 1e6 ceq of either OVA:DLE or BSA:DLE was added; IL-17A concentrations at 72 h measured and depicted as the change from media control. Antigen-naïve splenocytes were assayed independently from at least 3 mice/group. Data shown are representative of 3 or more independent experiments and displayed as means ± sem. Significance shown versus media control baseline or as indicated. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, as determined by ANOVA.