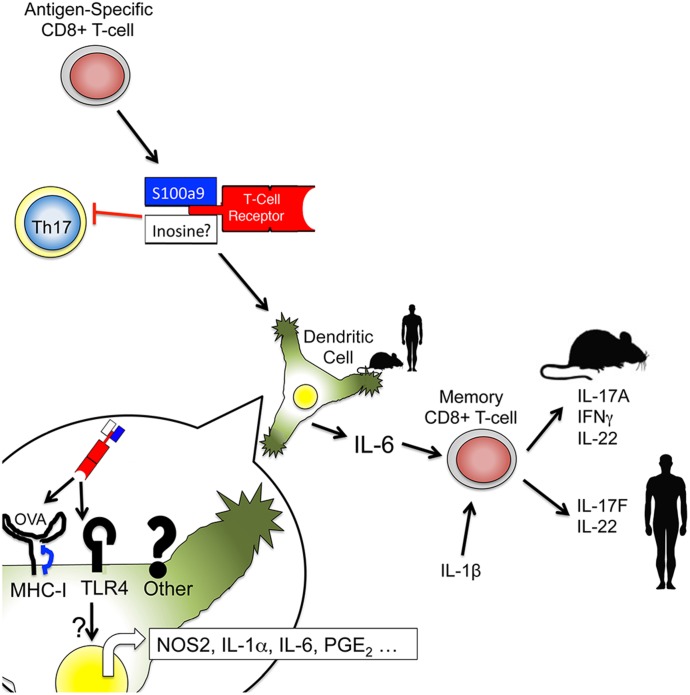
Figure 9. Proposed model of DLE activity.
Antigen-specific CD8+ T cells produce an antigen-specific activator of DCs. An antigen-binding region, likely derived from the TCR-β of the source CD8+ T cell, binds to the cognate antigen presented by DCs. Once bound by the DC, associated DLE molecules, such as S100a9-derived peptides or inosine/hypoxanthine, activate the DC to produce inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6. This cytokine response activates bystander memory CD8+ T cells in a contact- and TCR-independent manner, stimulating the production of IL-17 family cytokines.