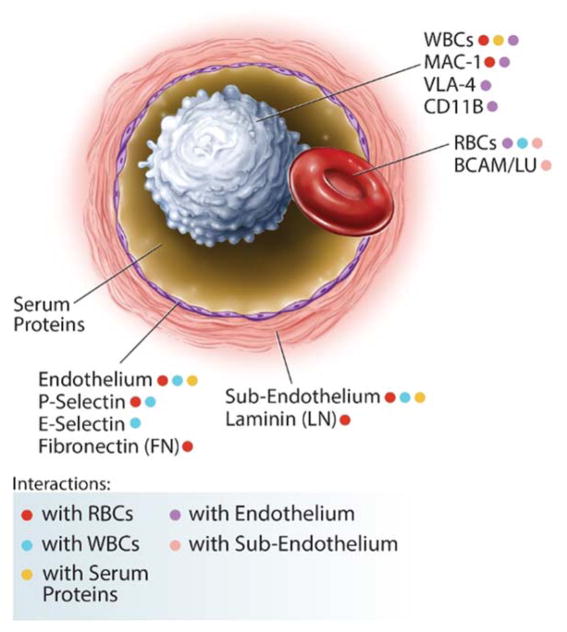
Figure 1. A subset of interactions between cellular and sub-cellular components in SCD.
Abnormal interactions, amongst HbS-containing RBCs, soluble serum proteins (such as thrombospondin, TSP, and von Willebrand Factor, vWF), cytokine- and WBC- (CD11b+ monocytes) activated endothelial cells (through integrins, integrin receptors, adhesion molecules, and selectins), subendothelial matrix components (including TSP, vWF, fibronectin, and laminin), and activated WBCs (via MAC-1+, LFA-1+, VLA-4+ neutrophils), which themselves also directly adhere to the endothelium.