Figure 1.
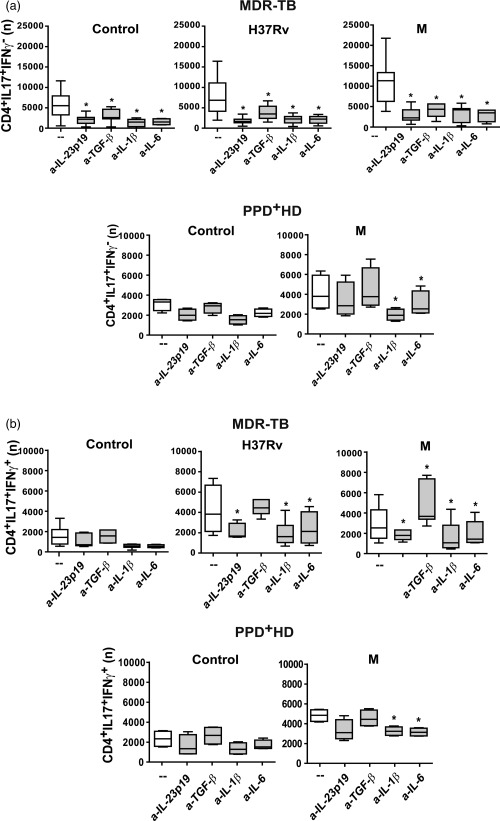
Interleukin (IL)‐23, transforming growth factor (TGF)‐β, IL‐6 and IL‐1β participate differentially in Mycobacterium tuberculosis‐induced T helper type 17 (Th17) response. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 31 multi‐drug‐resistant tuberculosis (MDR‐TB) and eight purified protein derivative (PPD)+ healthy donors (HD) were stimulated for 48 h alone (control) or with H37Rv and M strains (2 : 1 bacteria to PBMC ratio), in the absence (–) or presence of antibodies against IL‐23p19, TGF‐β, IL‐1β and IL‐6 (a‐IL‐23p19, a‐TGF‐β, a‐IL‐1β and a‐IL‐6, respectively). IL‐17 and interferon (IFN)‐γ expression was determined in CD4+ T cells by flow cytometry [fluorescence‐activated cell sorter (FACS)] and the number (n) of (a) CD4+IL‐17+IFN‐γ– and (b) CD4+IL‐17+IFN‐γ+ cells present in 1×106 cultured PBMC was calculated for each individual. Results are expressed as median and 25th–75th percentiles (boxes) with maximum and minimum values (error bars). Statistical differences: *P < 0·05 for treated versus non‐treated PBMC (Friedman test followed by Dunn's test).
