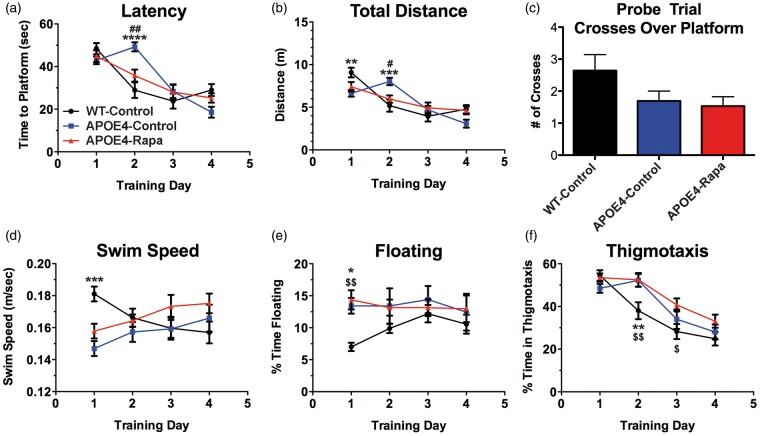
Figure 4.
Rapamycin ameliorates incipient learning phenotypes of APOE4 mice. (a) Time in seconds to reach a hidden platform. Time F (3, 117) = 37.51, P < 0.0001; Treatment F (2, 39) = 0.496, P = 0.613; Interaction F (6, 117) = 5.919, P < 0.0001; (b) total distance swam during trial. Distance F (3, 117) = 30.06, P < 0.0001; treatment F (2, 39) = 0.079, P = 0.024; interaction F (6, 117) = 5.704, P < 0.0001; (c) number of times mice crossed over the platform location in the probe trial. n.s., P = 0.091; (d) average swim speeds during training. Speed F (3, 117) = 0.416, P = 0.742; treatment F (2, 39) = 1.59, P = 0.217; interaction F (6, 117) = 4.986, P < 0.0001; (e) percent of trial spent floating. Time floating F (3, 117) = 0.821, P = 0.485; treatment F (2, 39) = 2.601, P = 0.087; interaction F (6, 117) = 1.19, P = 0.316; (f) percent of trial spent in thigmotaxis. Time in thigmotaxis F (3, 117) = 39.25, P < 0.0001; treatment F (2, 39) = 5.92, P = 0.006; interaction F (6, 117) = 2.212, P = 0.047. Data are presented mean ± standard error of the mean of 4 trials/animal/day. All asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference between WT-control vs. APOE4-control, all pound signs (#) indicate a significant difference between APOE4-control vs. APOE4-Rapa, and all money signs ($) indicate a significant difference between WT-control vs. APOE4-Rapa. Behavioral data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.
APOE4: apolipoprotein E4.